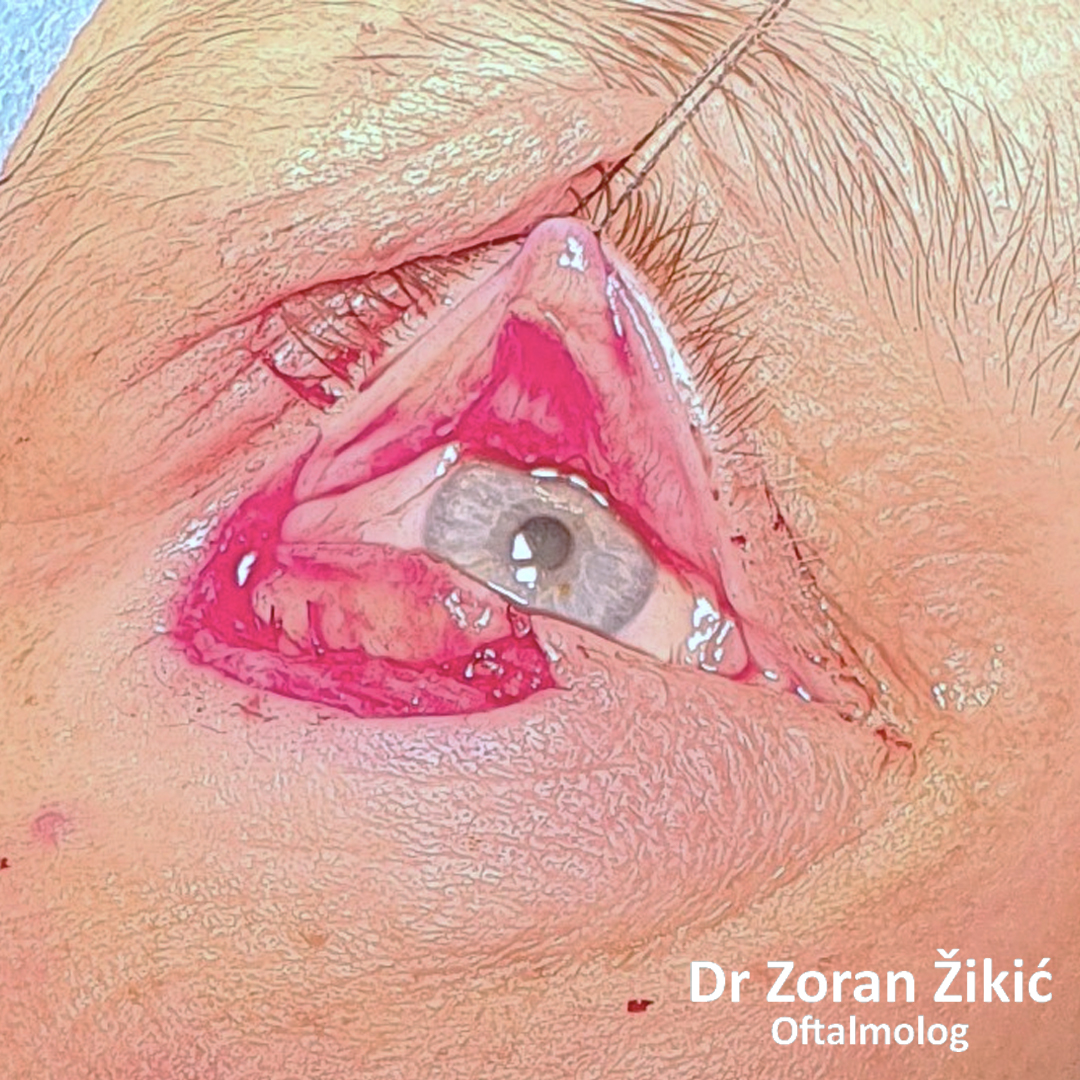
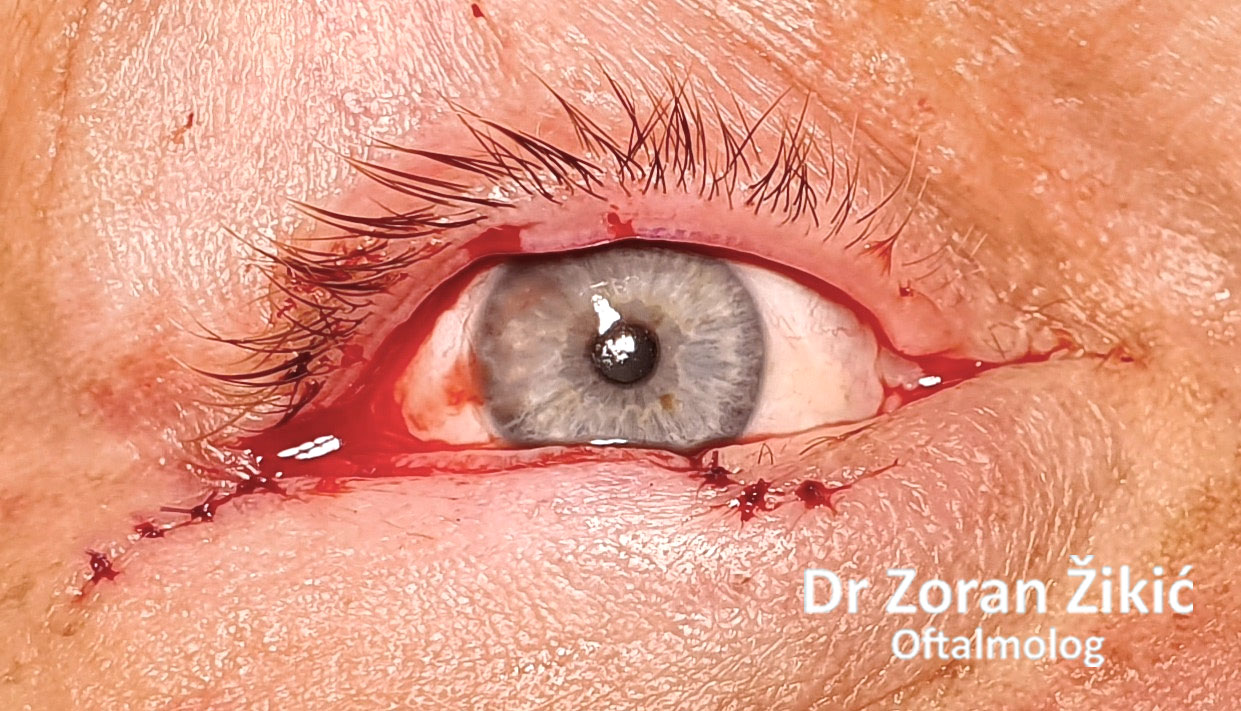
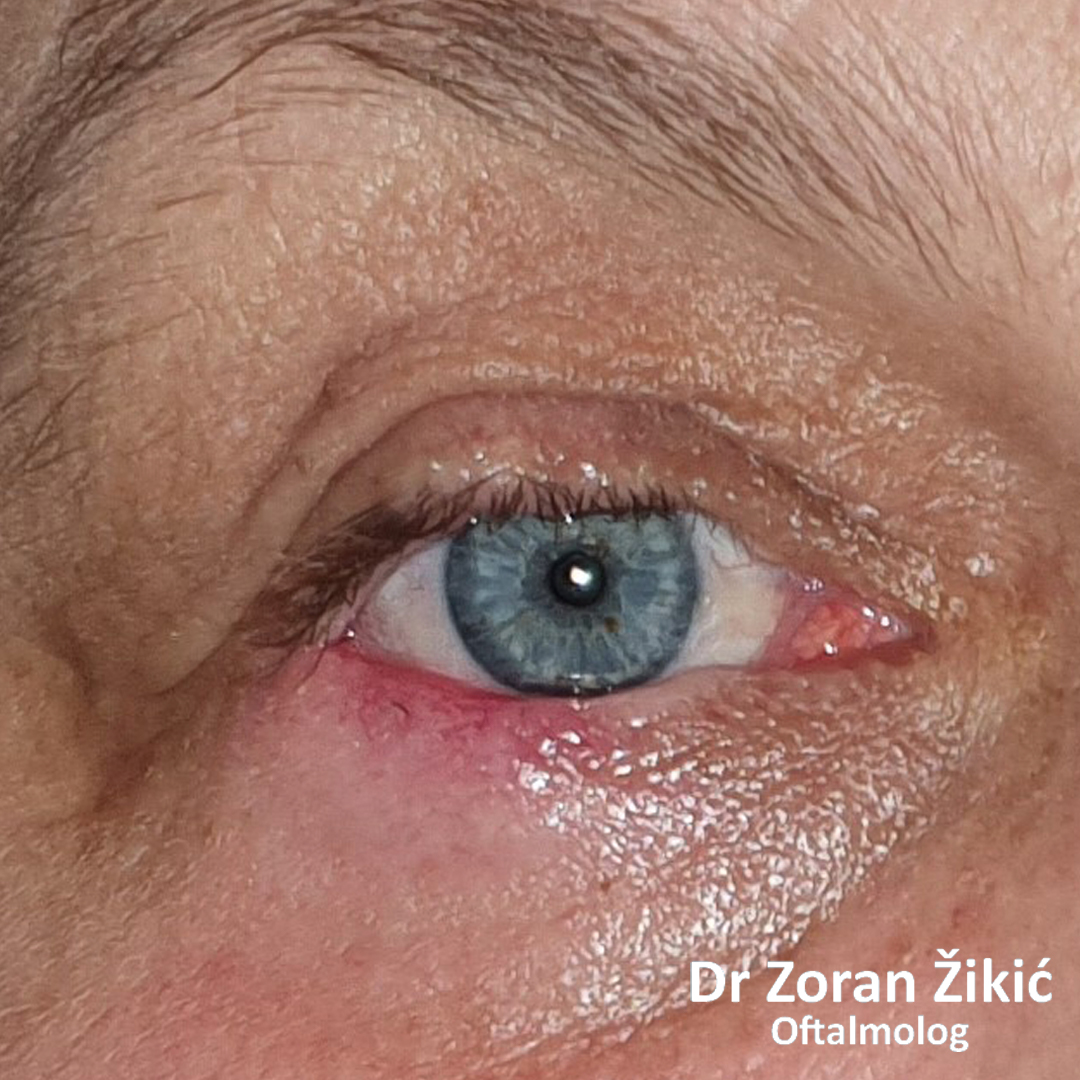
LOWER LID BLEPHAROPLASTY
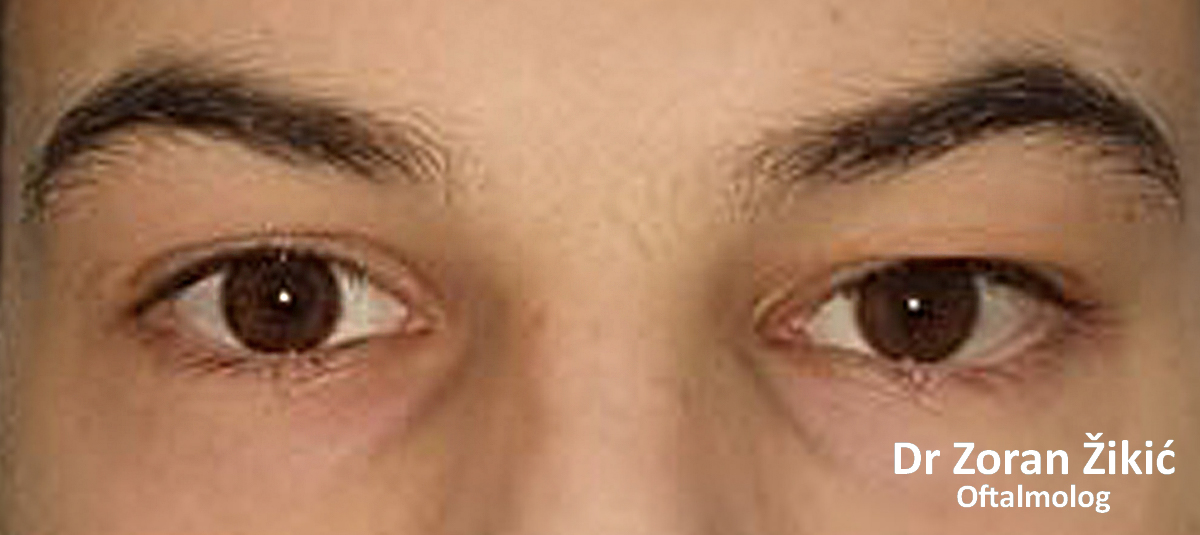
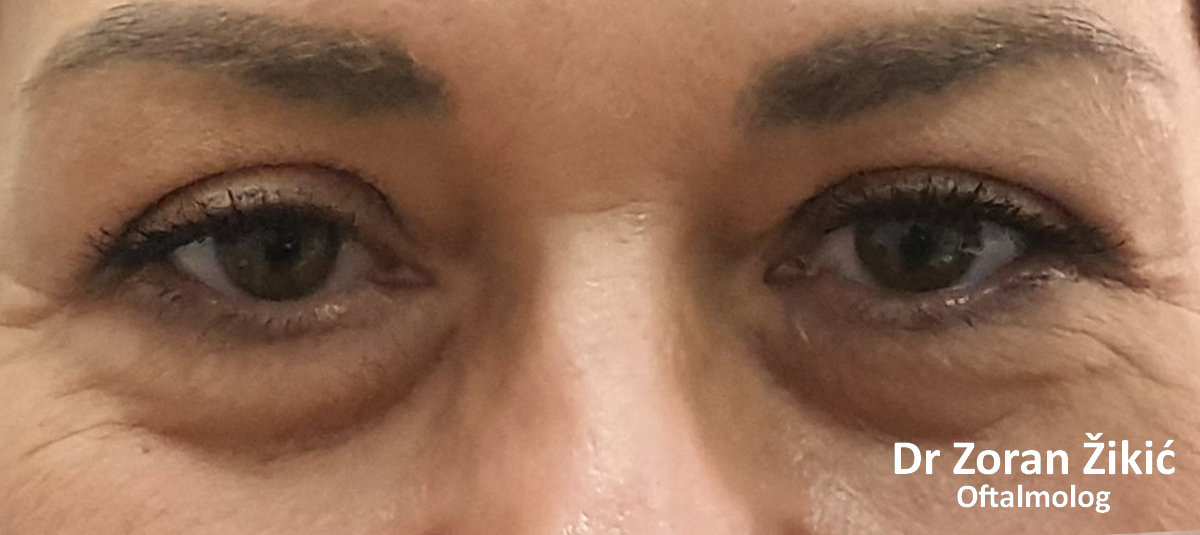
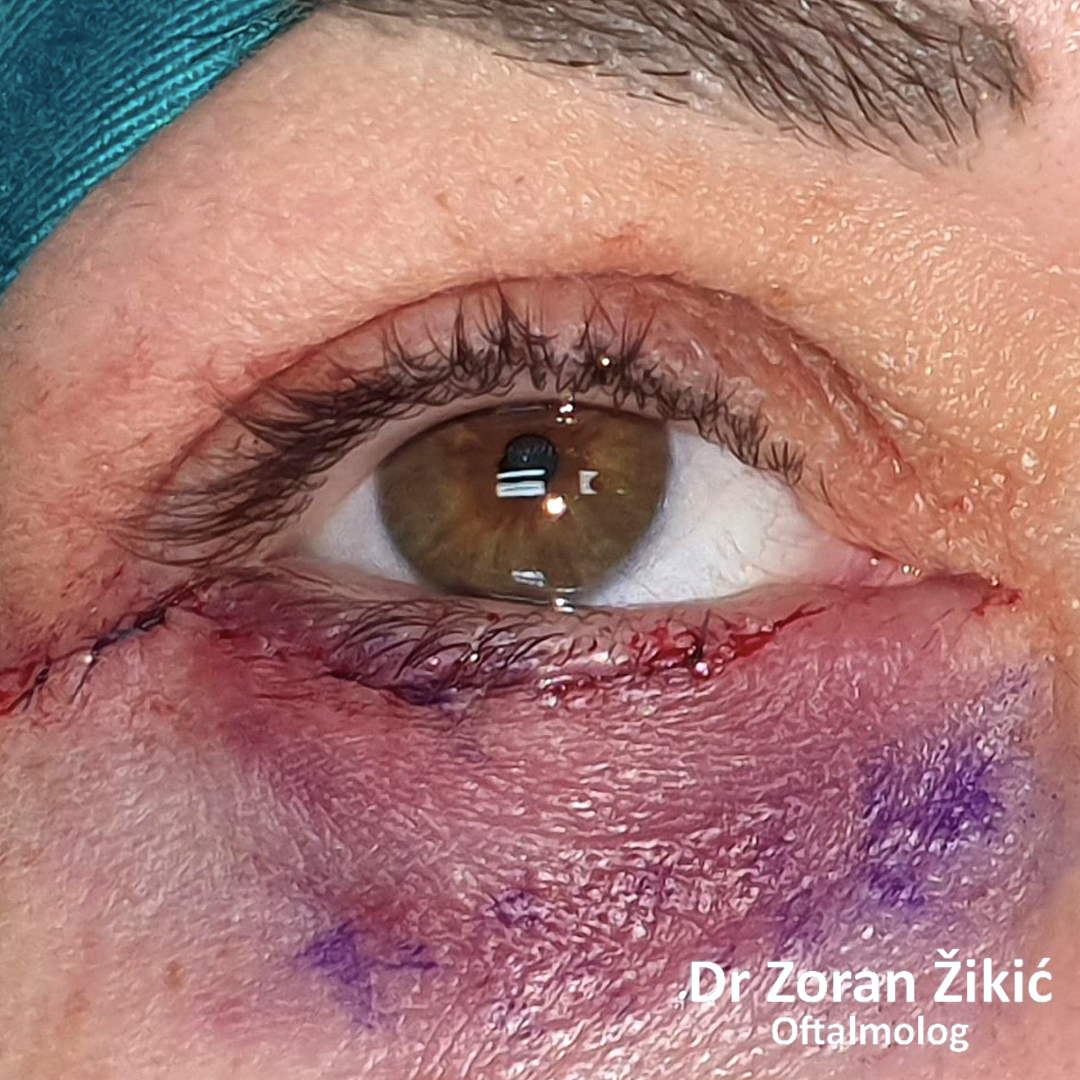
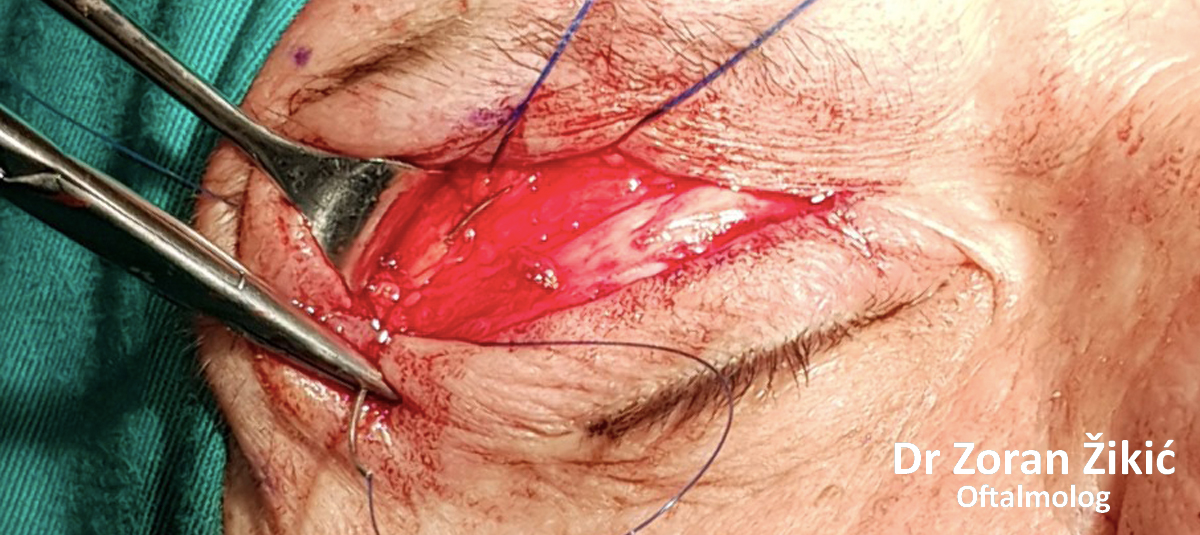
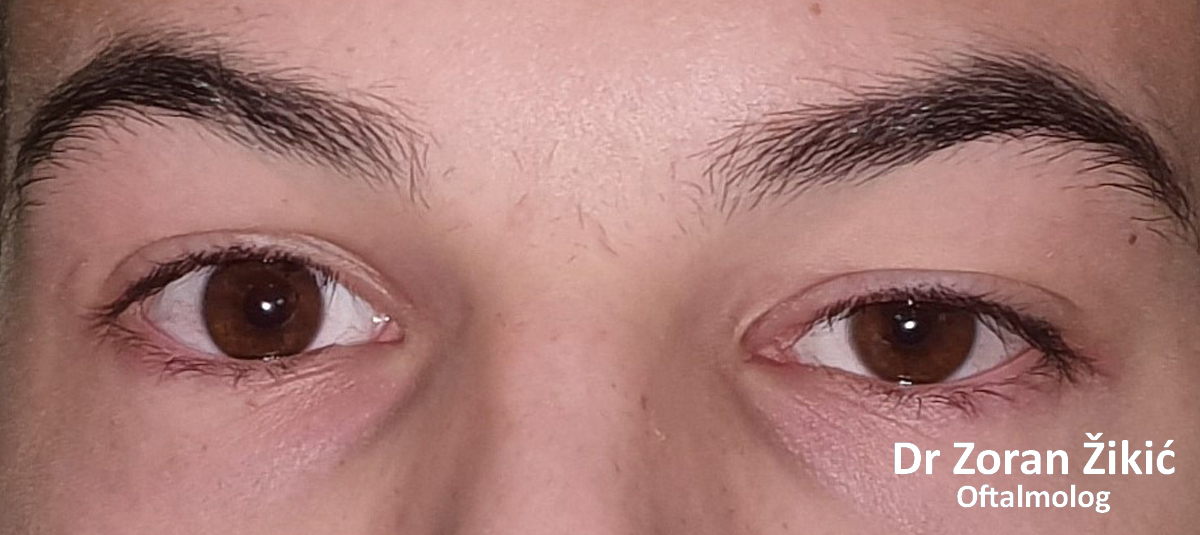
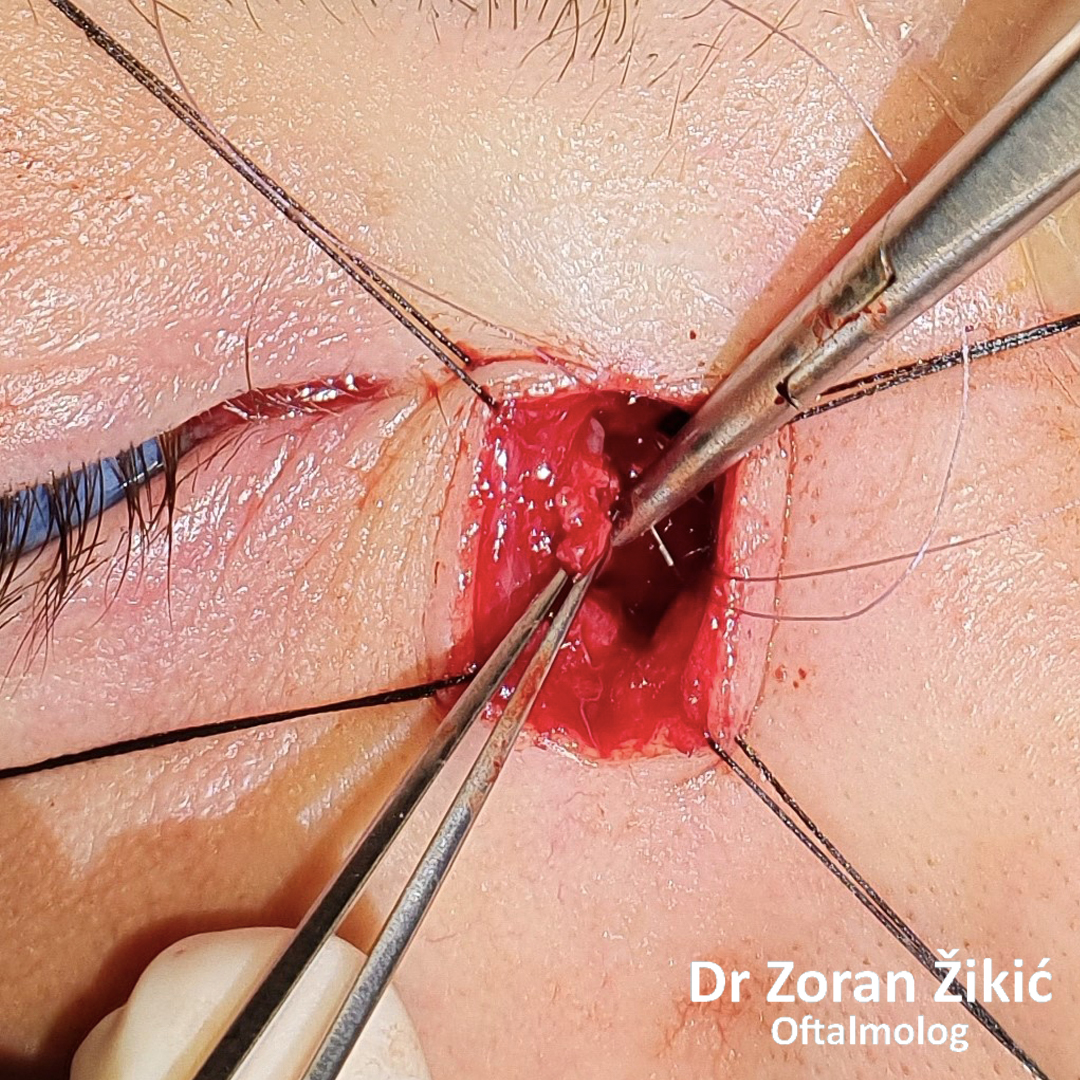
Lower lid bags and deep „tear trough“ (junction between lid and cheek).
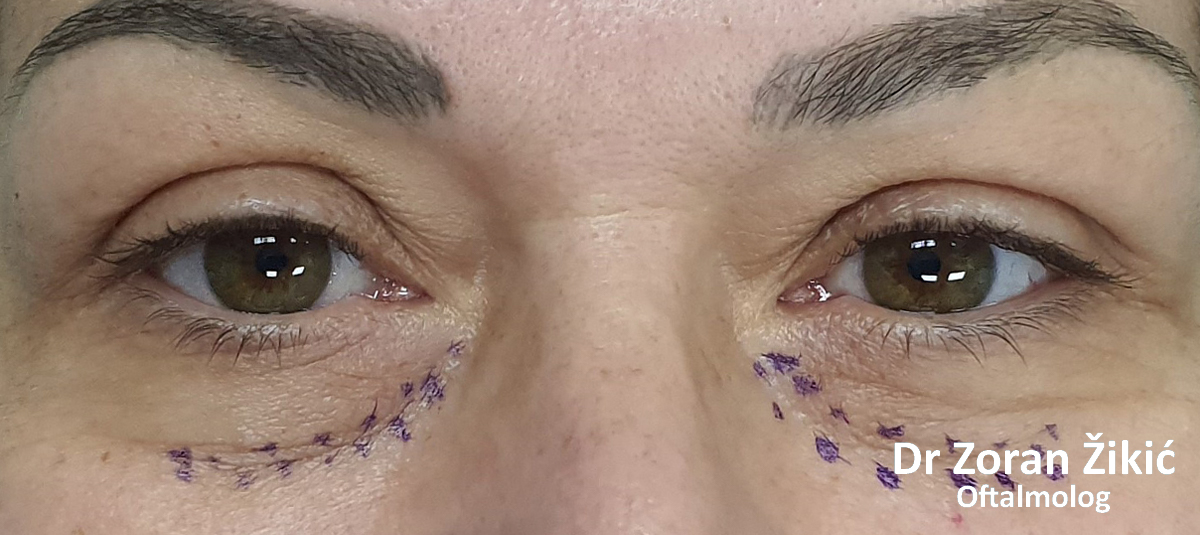
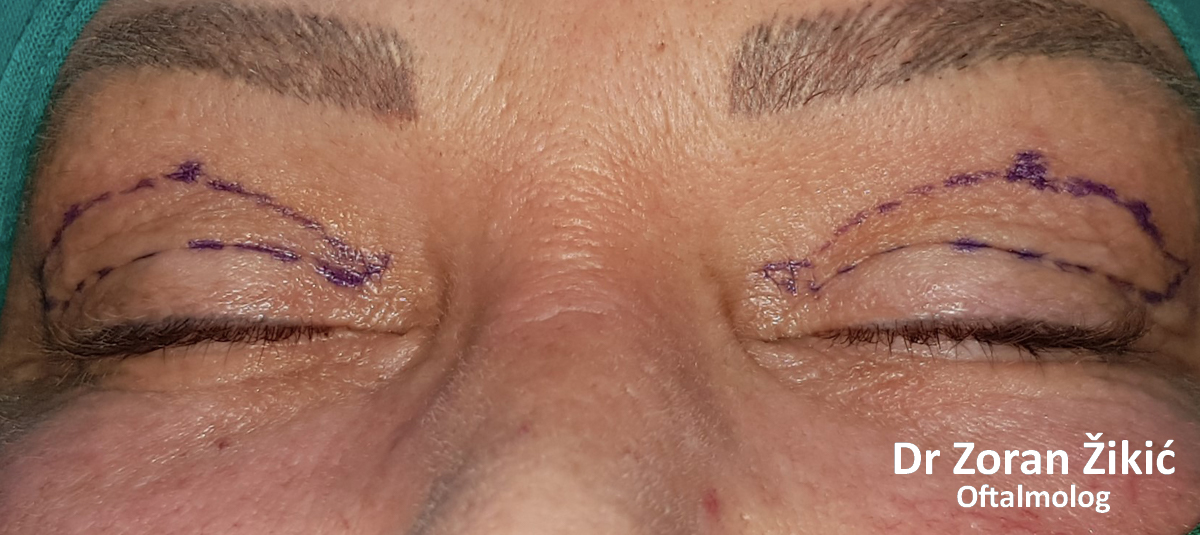
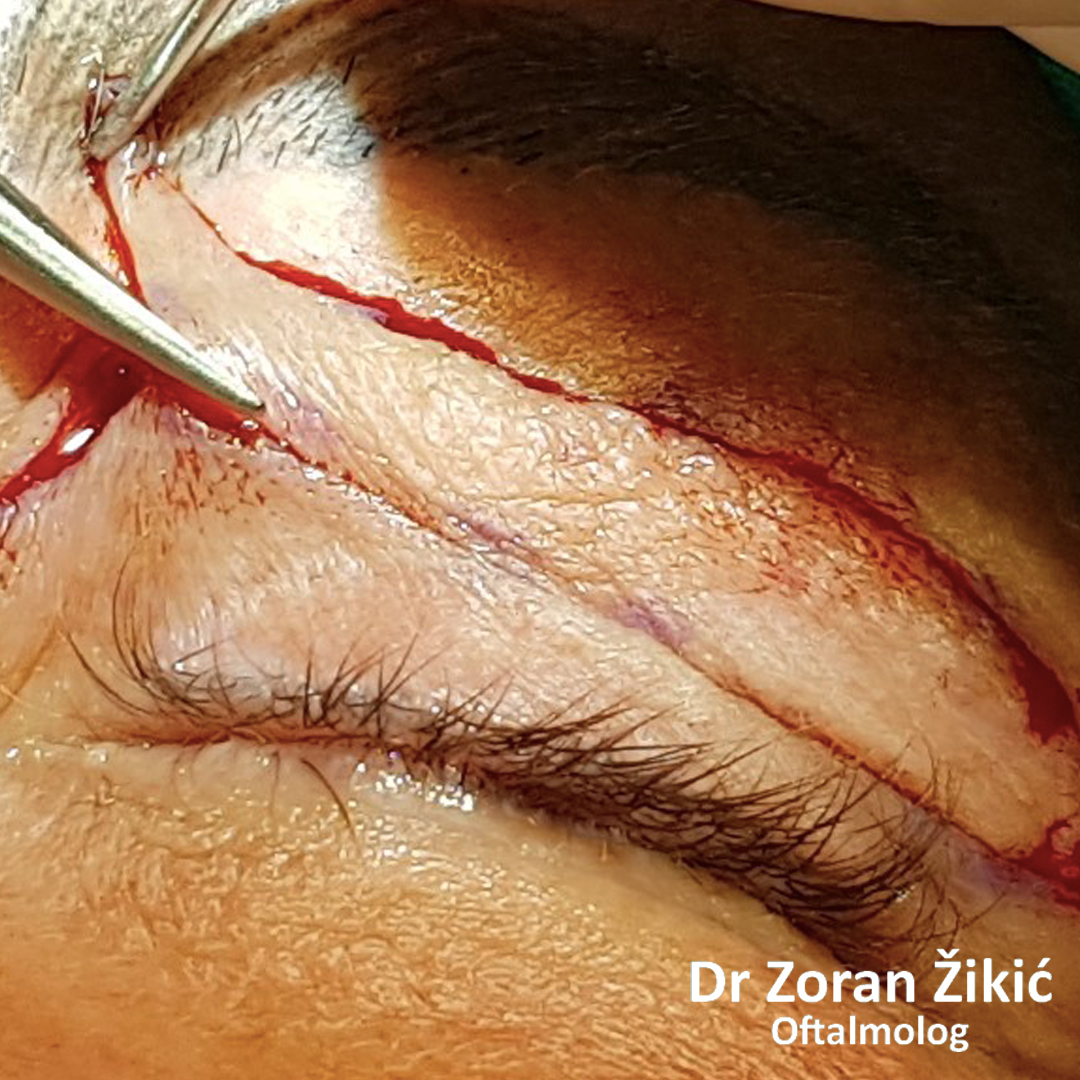
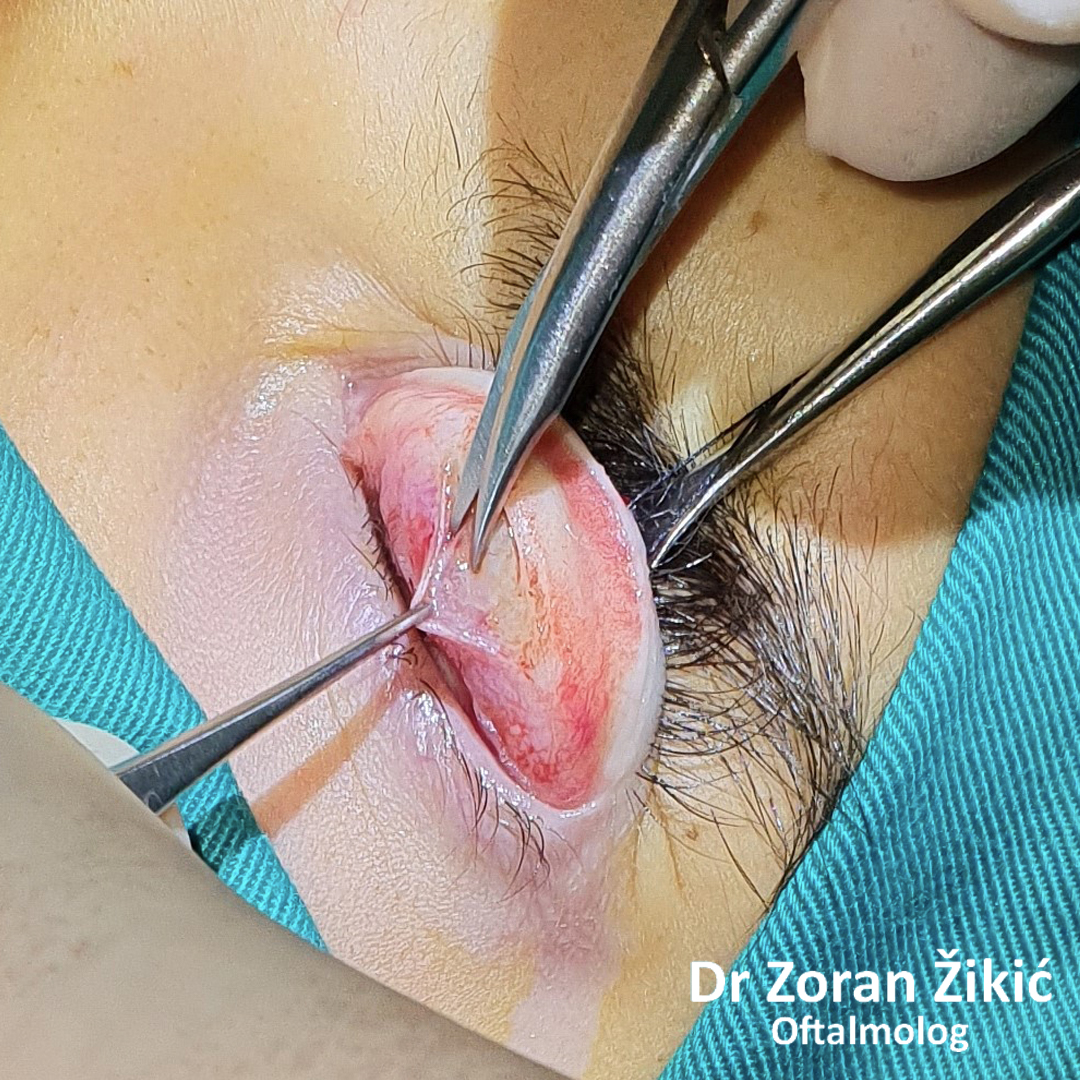
Pre-operative markings of the hollow area, which needs to be
filled with transposed fat.
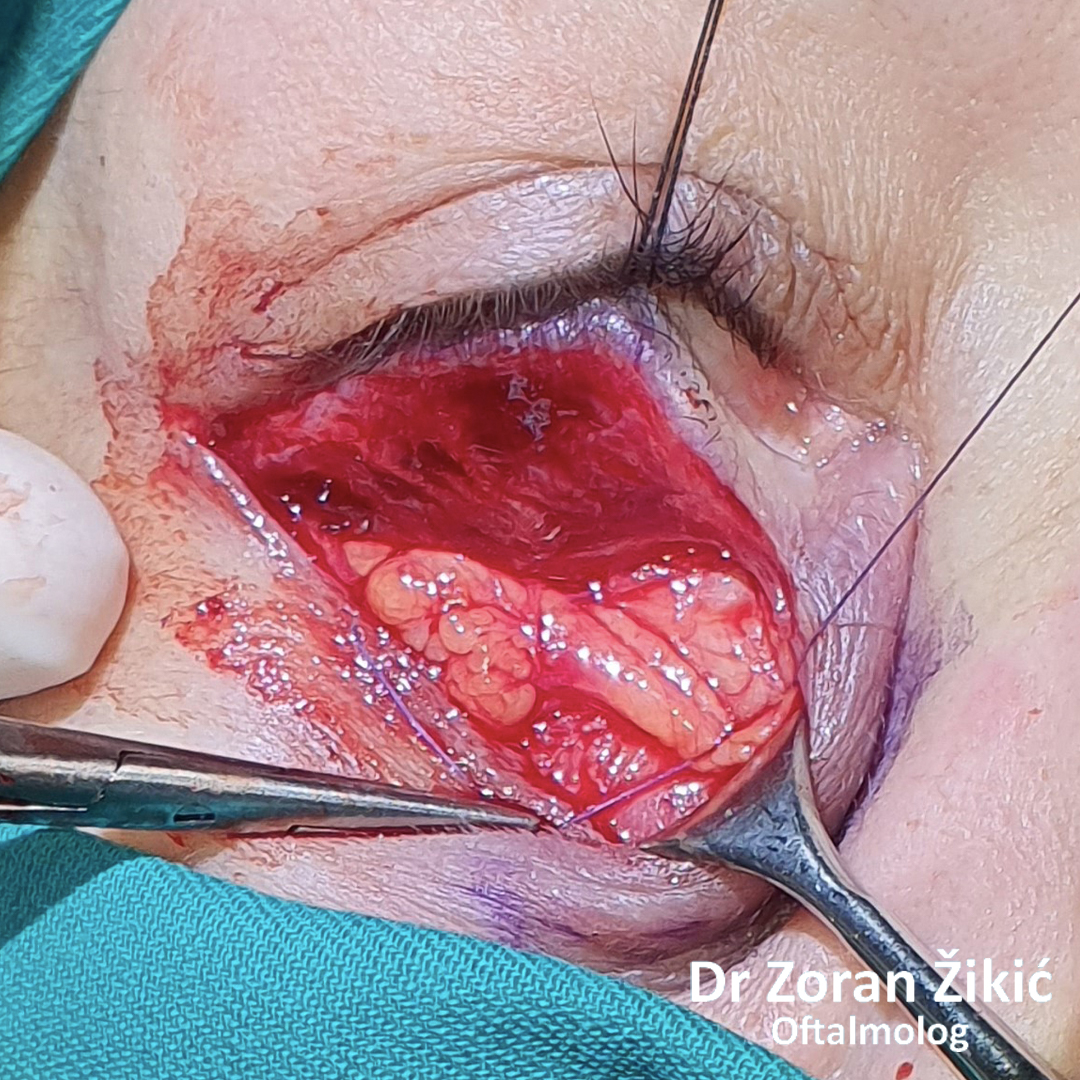
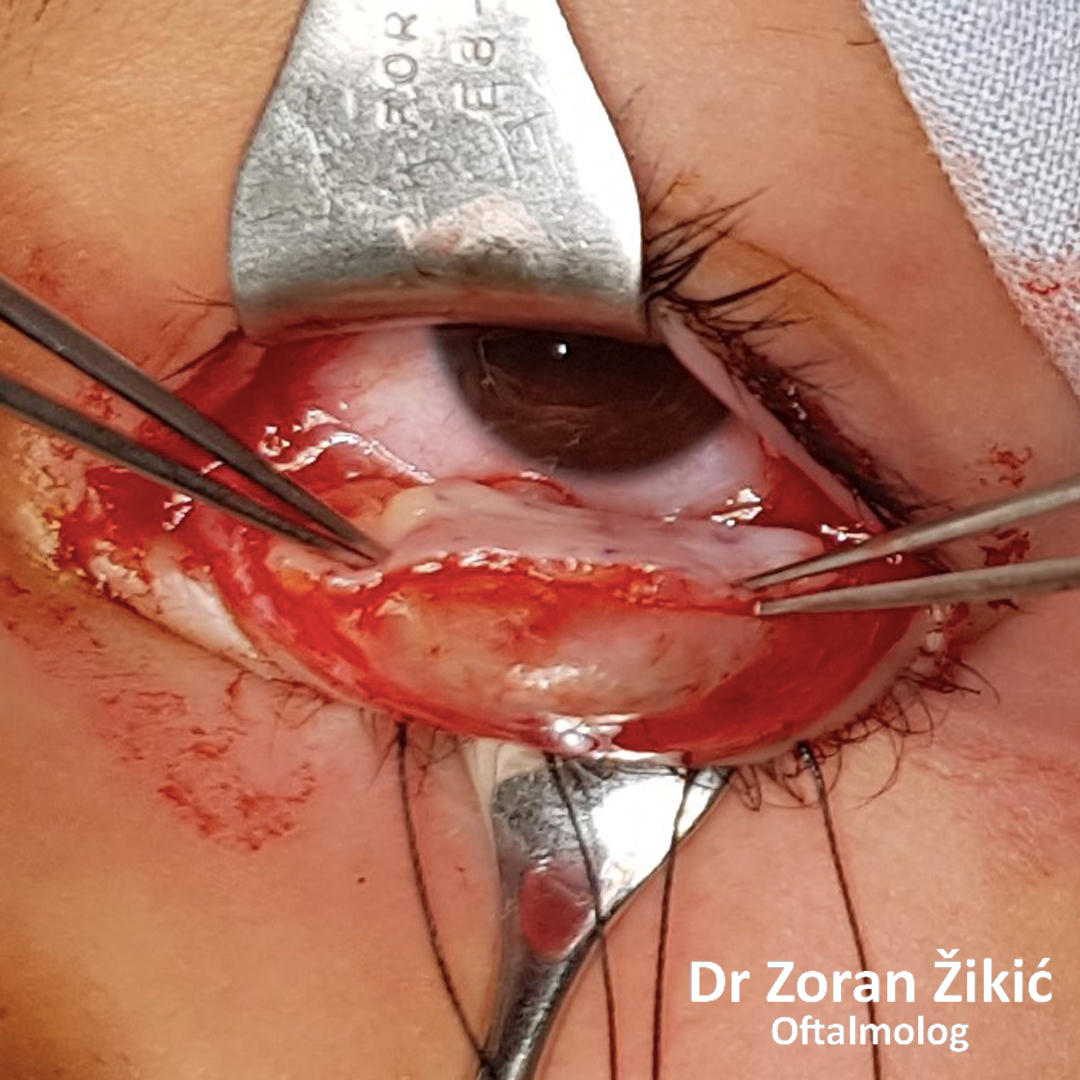
The fat, which forms the lower lid bag, is not exscised, but is „transposed“
into the hollow.
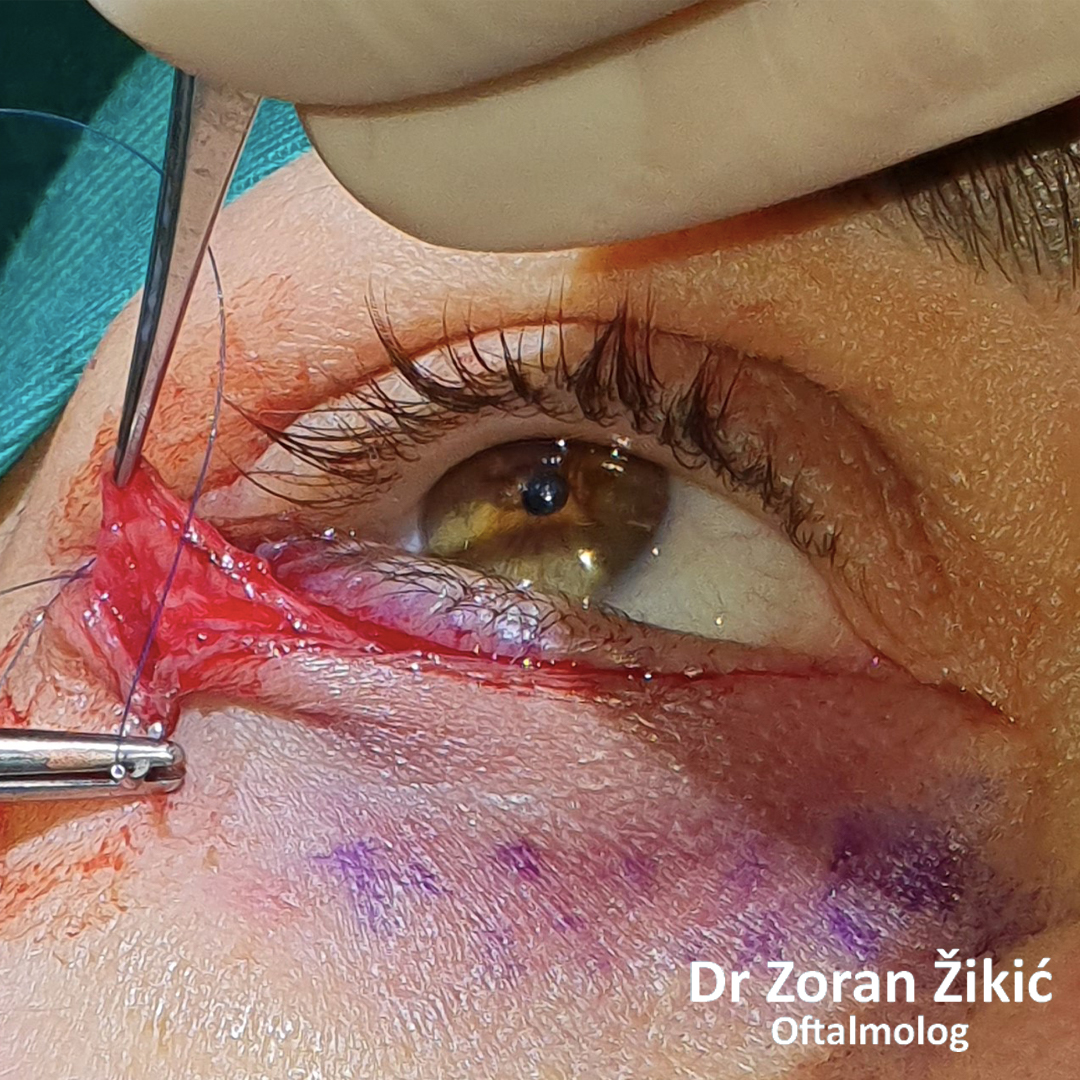
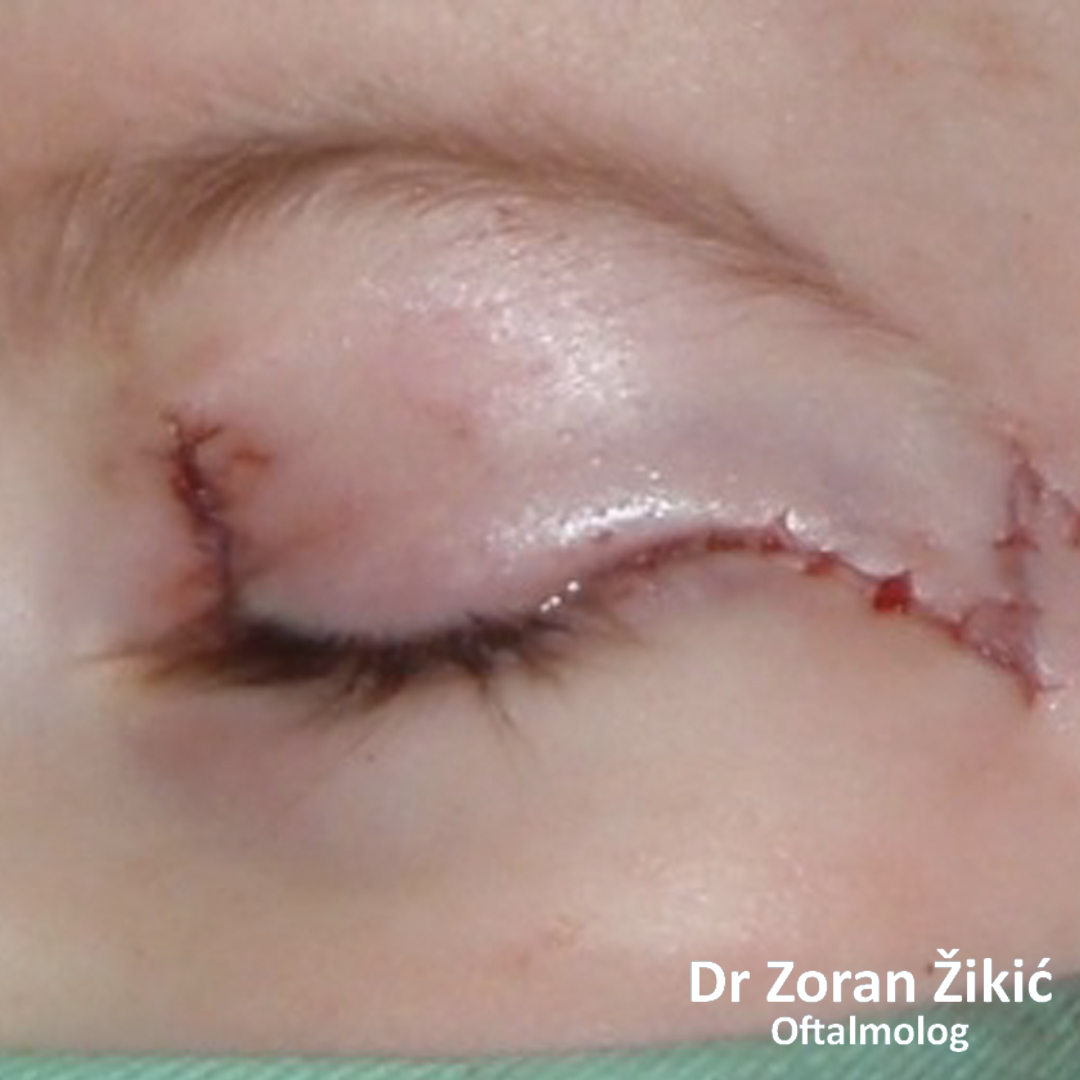
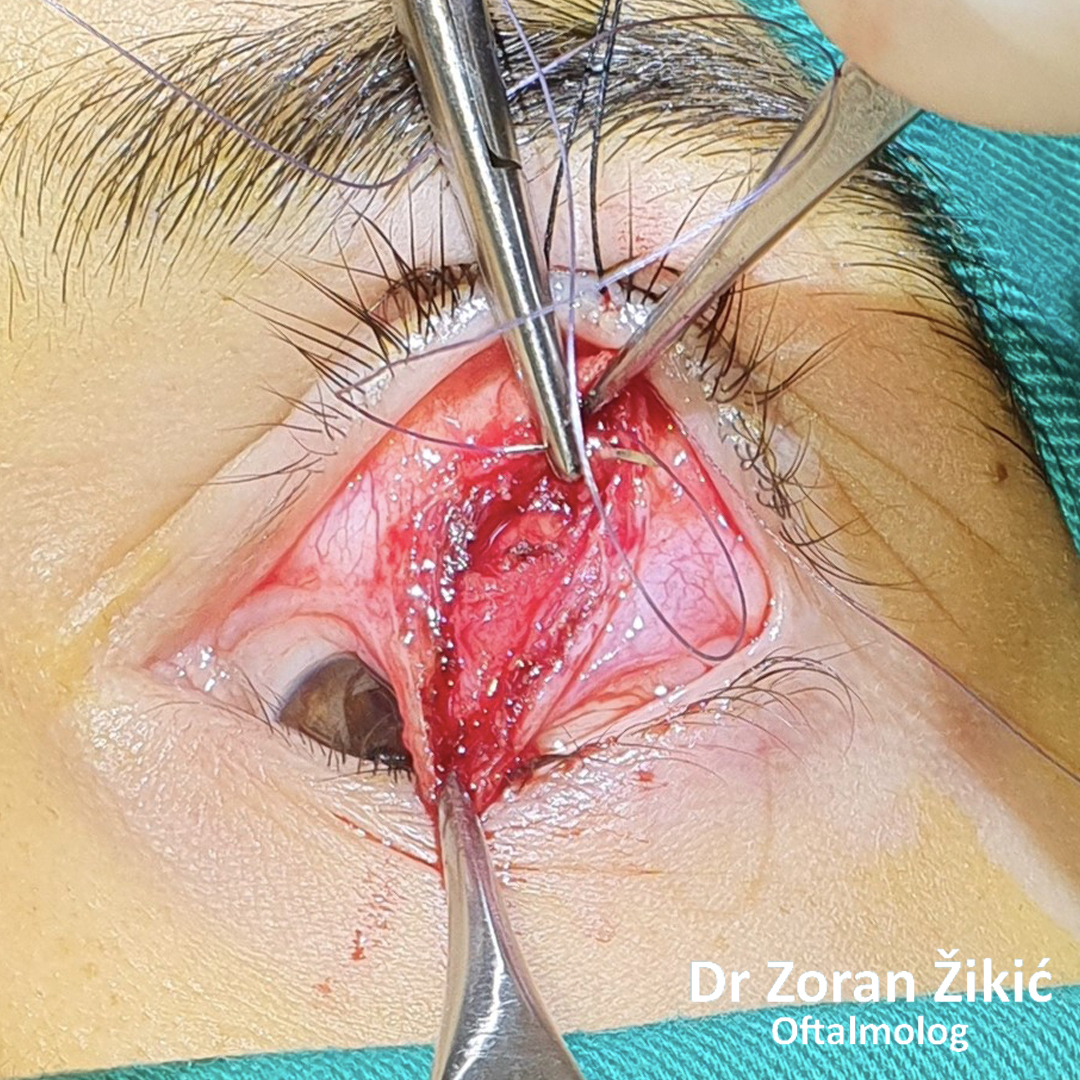
The lid itself and the lid muscle (orbicularis) are tightened.
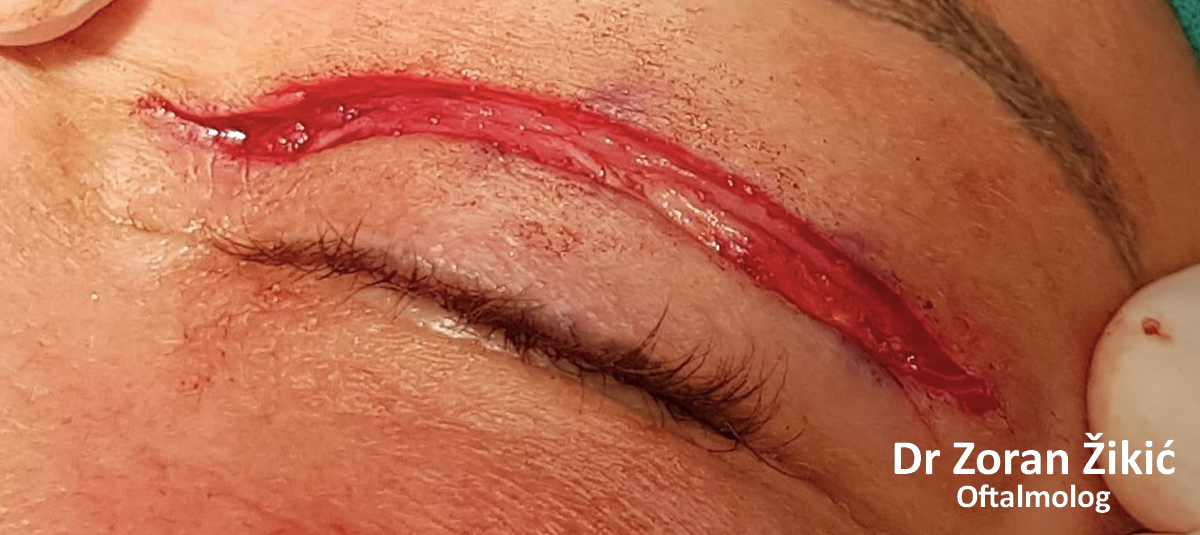
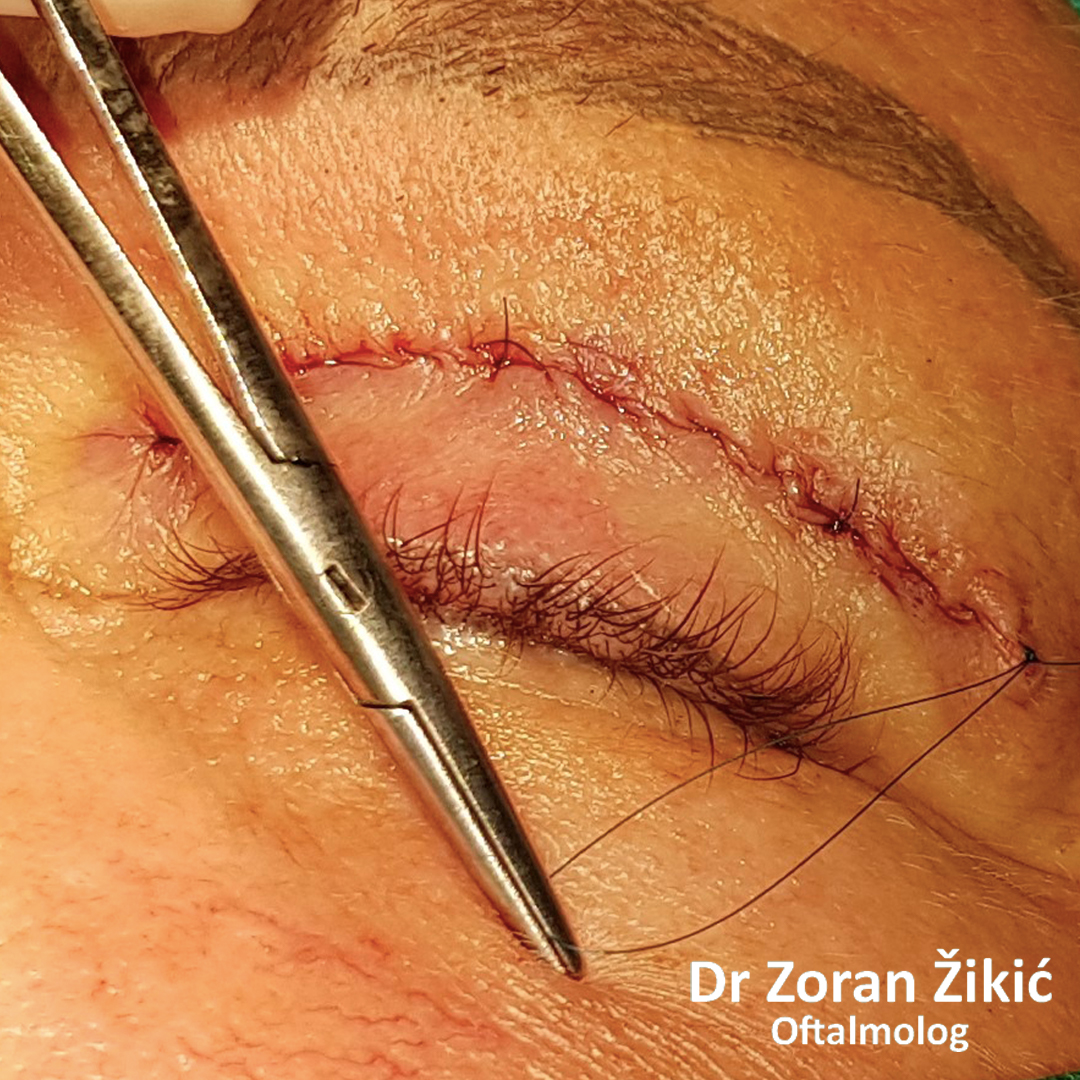
After minimal „excess“ skin exscision, the sutures are placed.
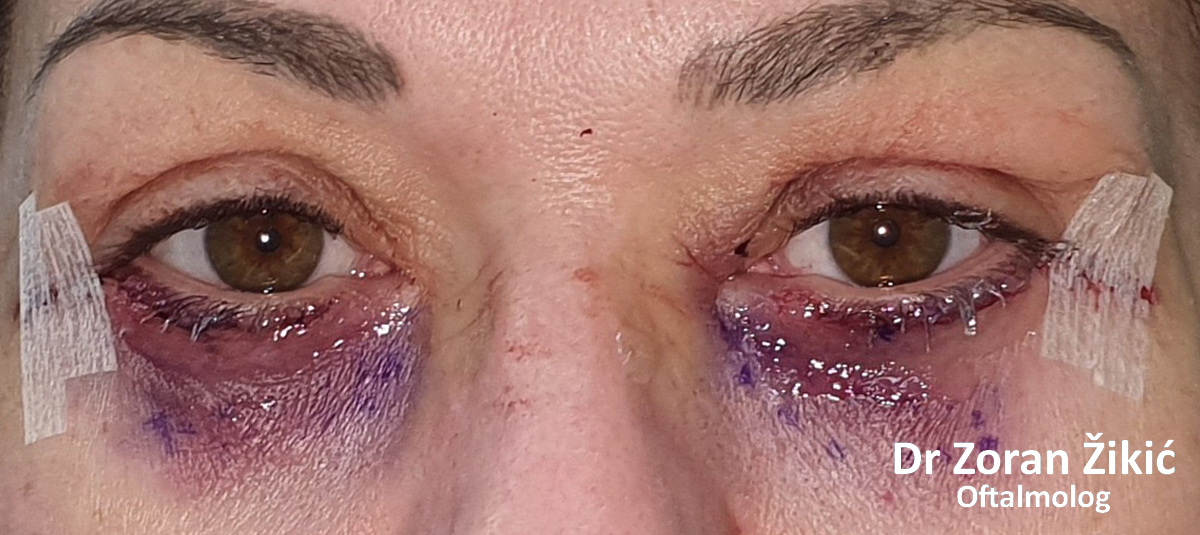
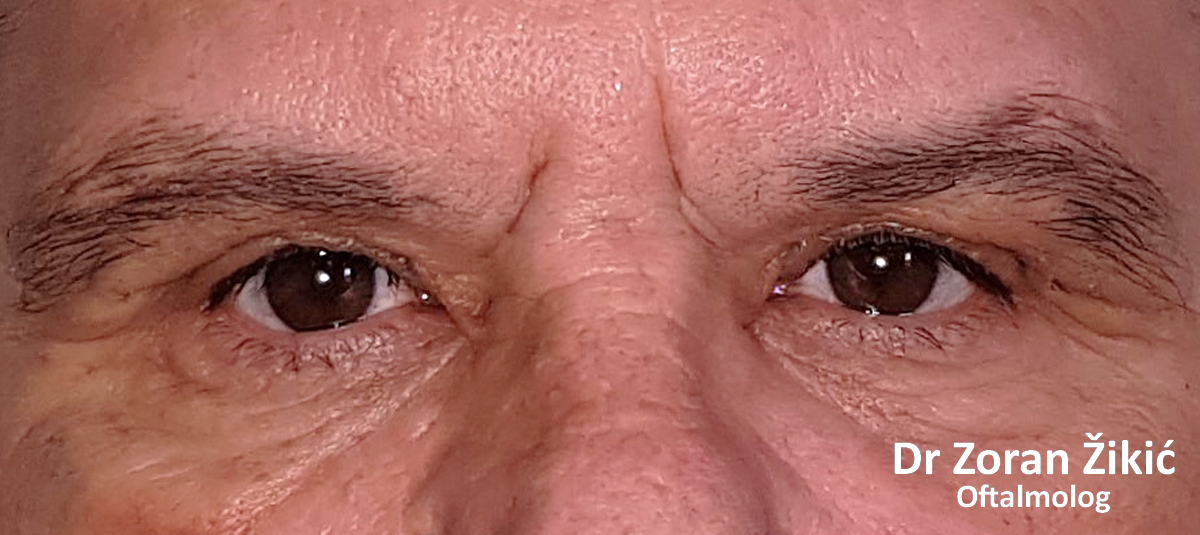
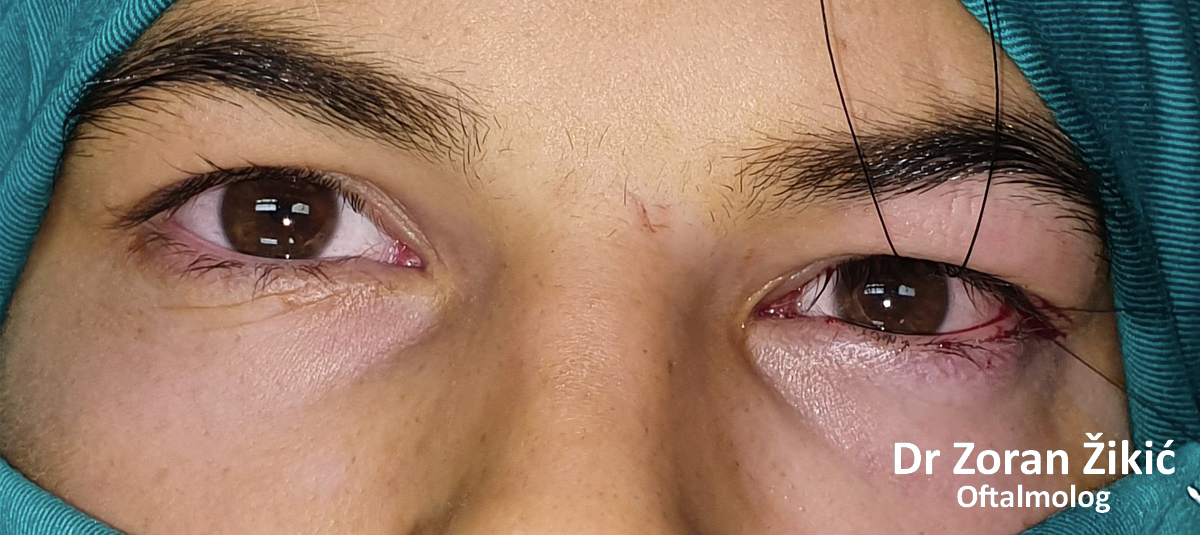
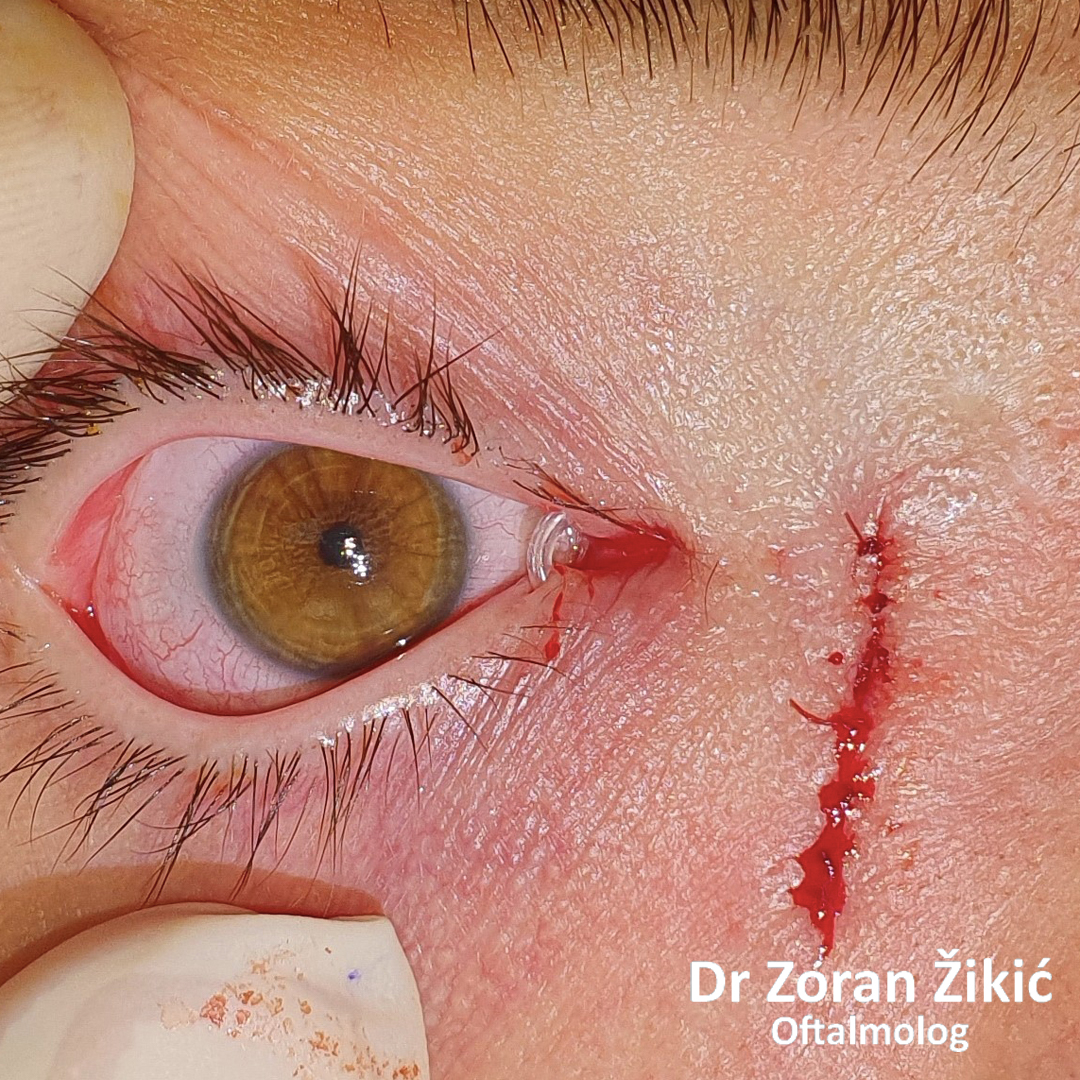
One day after surgery. Swelling and bruising are common.
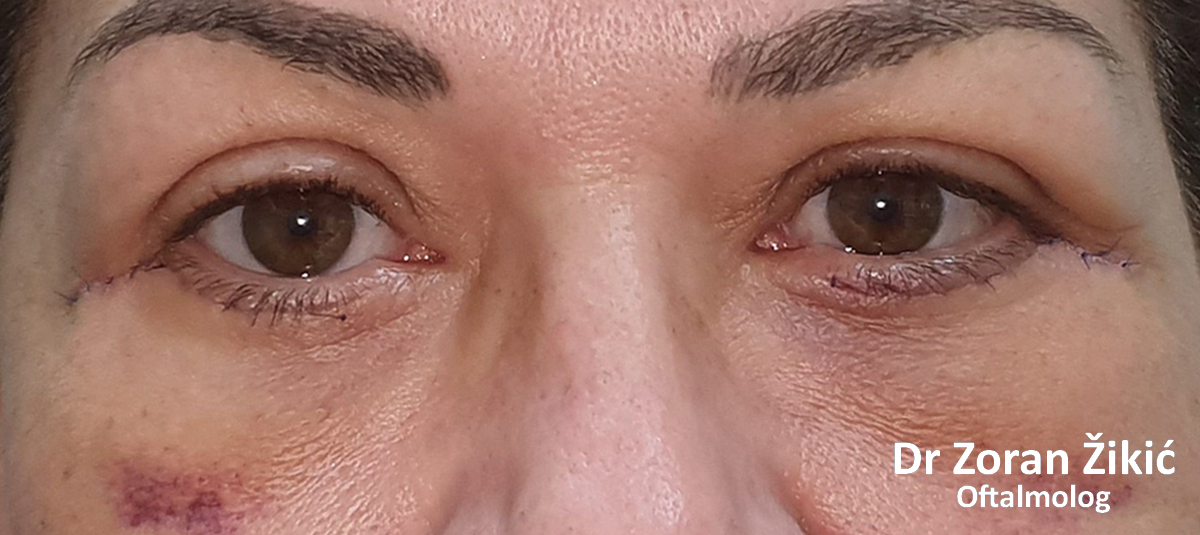
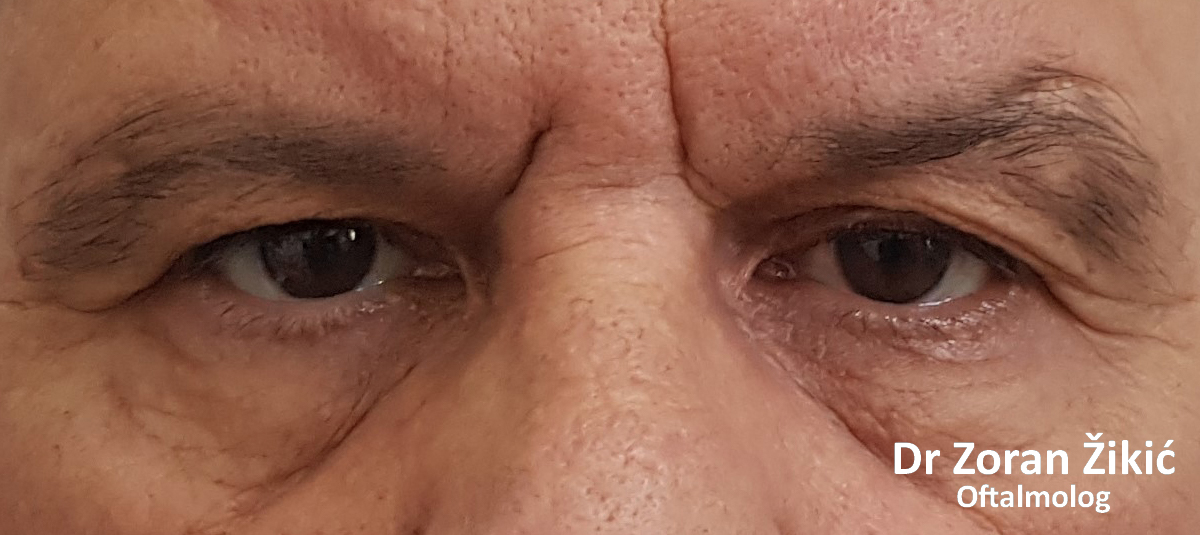
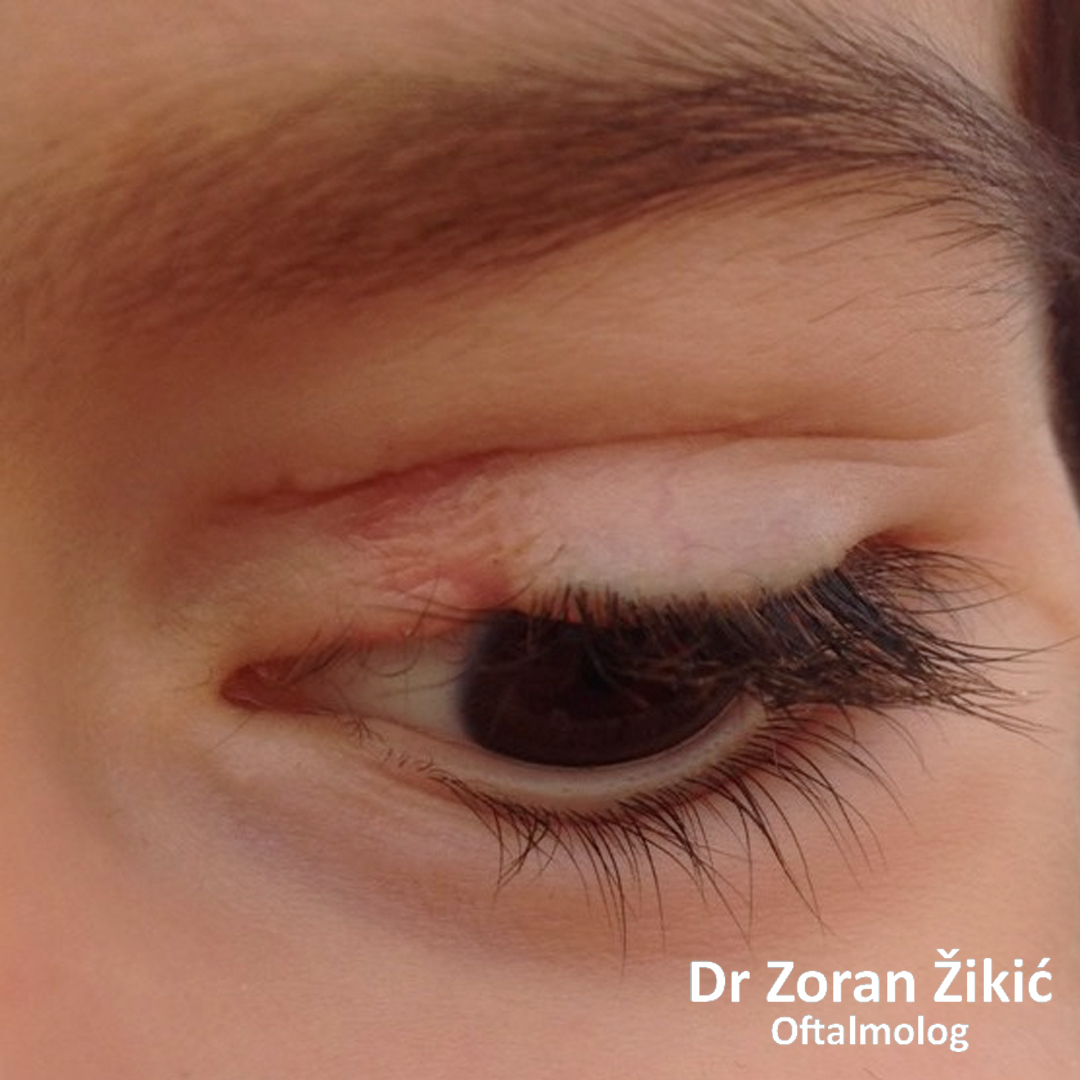
One week after surgery, before suture removal.
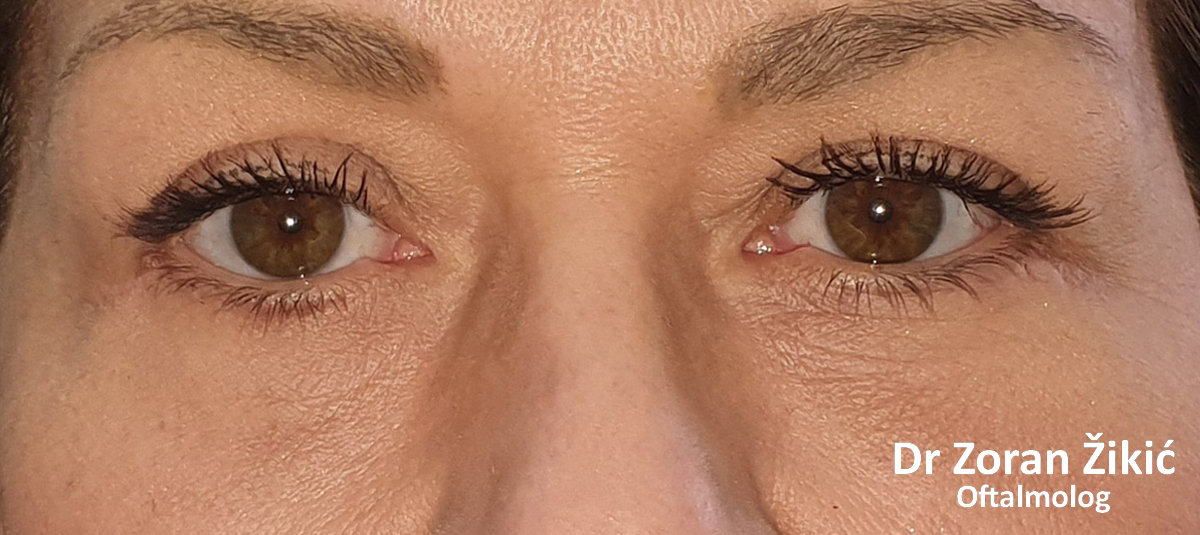
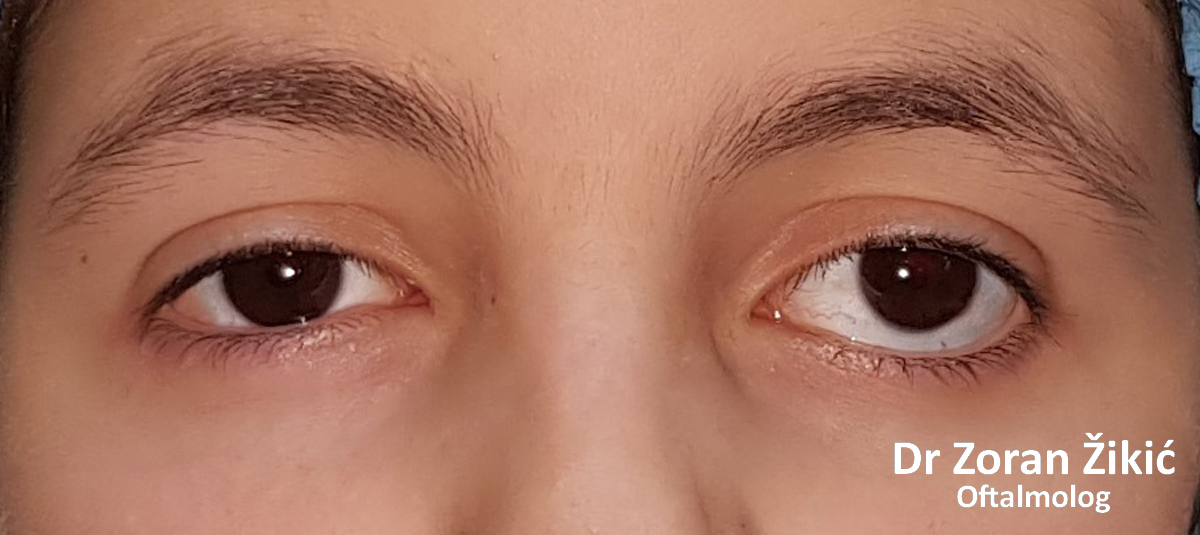
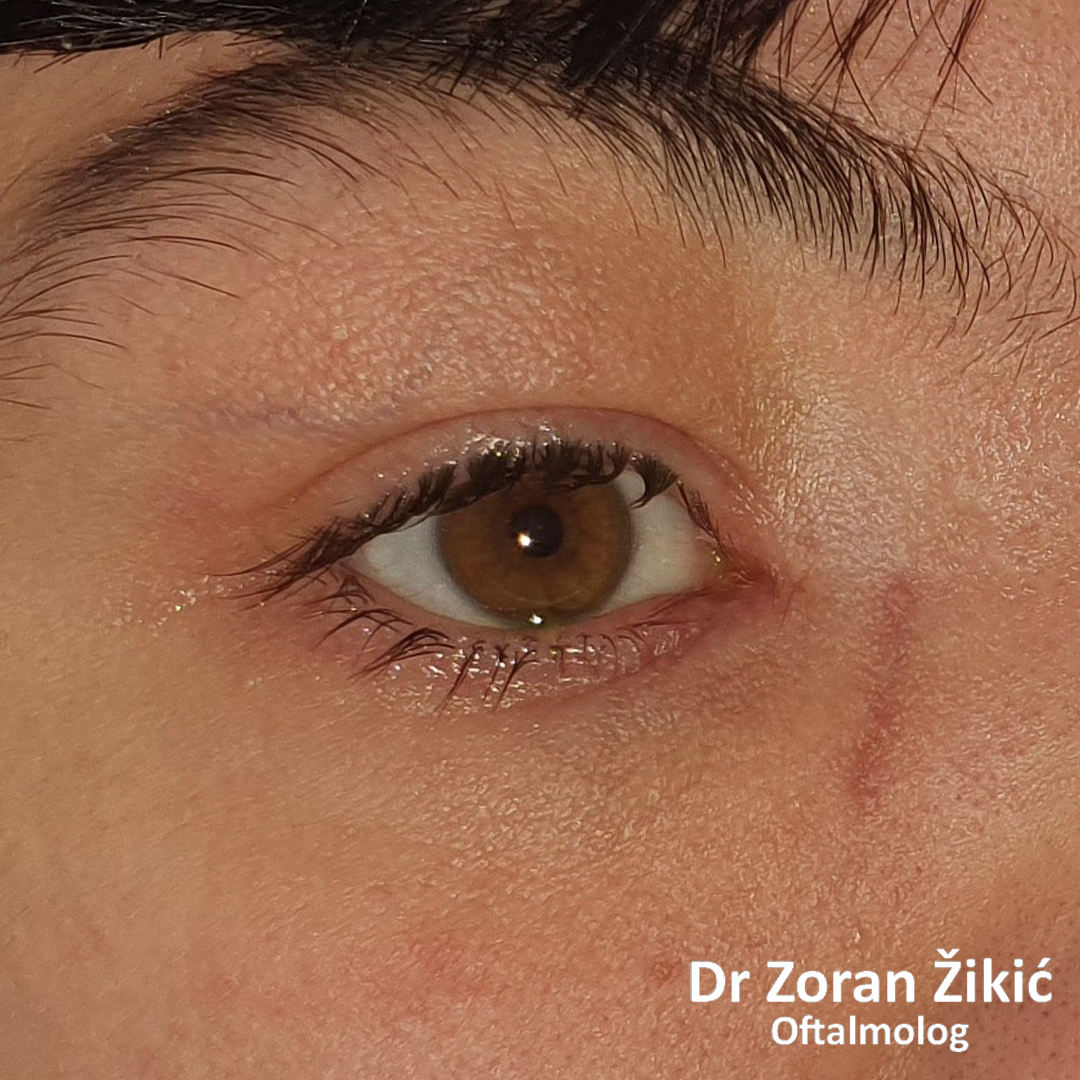
One month after the operation.
UPPER LID BLEPHAROPLASTY
Pre-operative skin marking.
After redundant skin exscision.
UPPER LID BLEPHAROPLASTY WITH INTERNAL BROW ELEVATION
Very „heavy“ eyebrows, which are depressing the upper lid skin.
During blepharoplasty, the eyebrows are elevated.
One month after the operation. The patient reports that the heavyness
Sensation in the eyebrow area is gone.
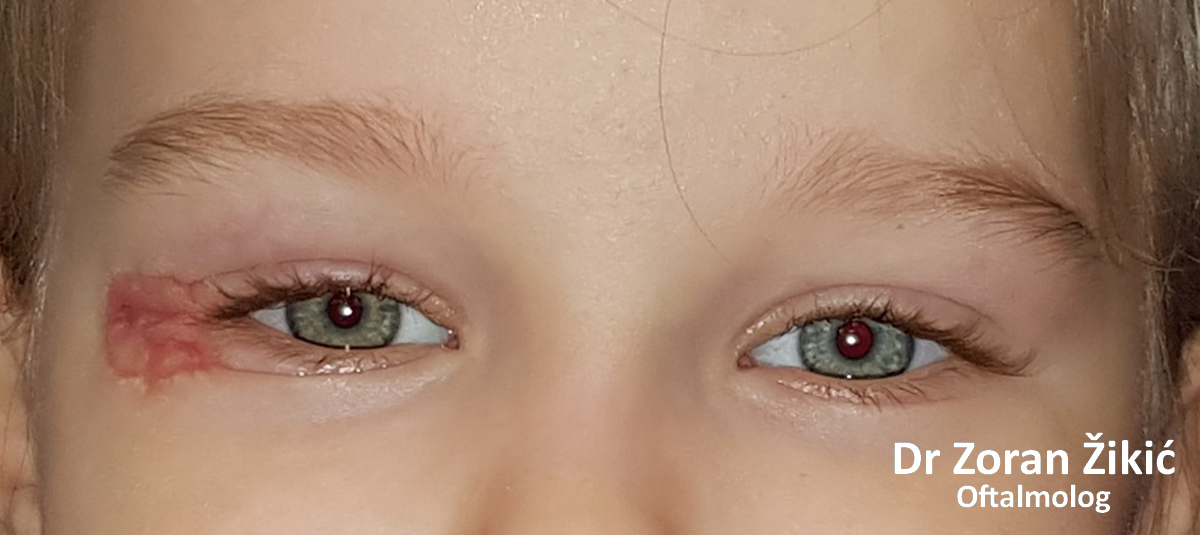
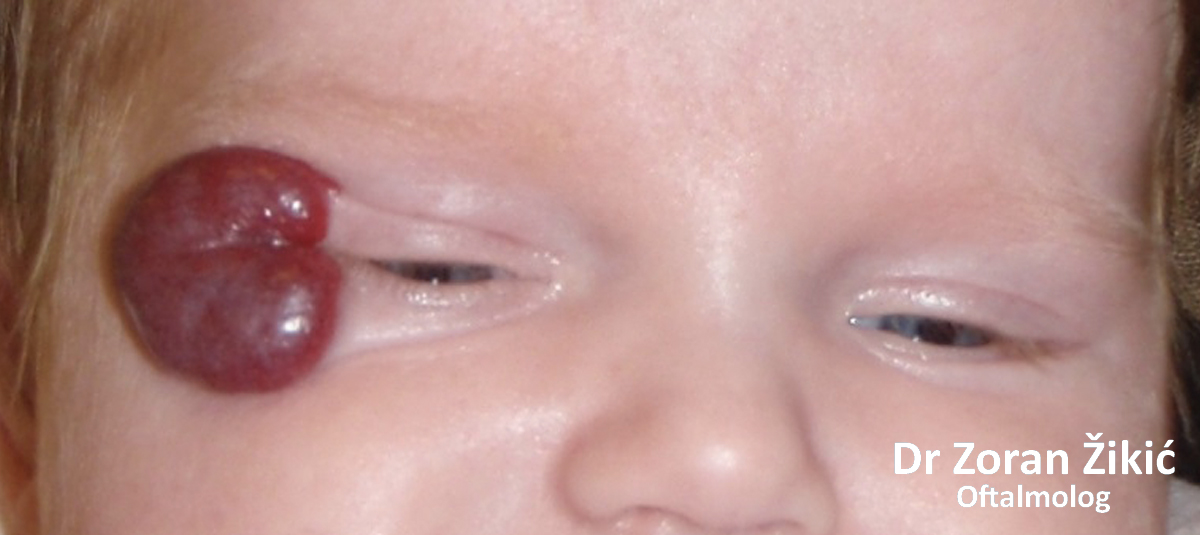
Hemangioma of the eyelids
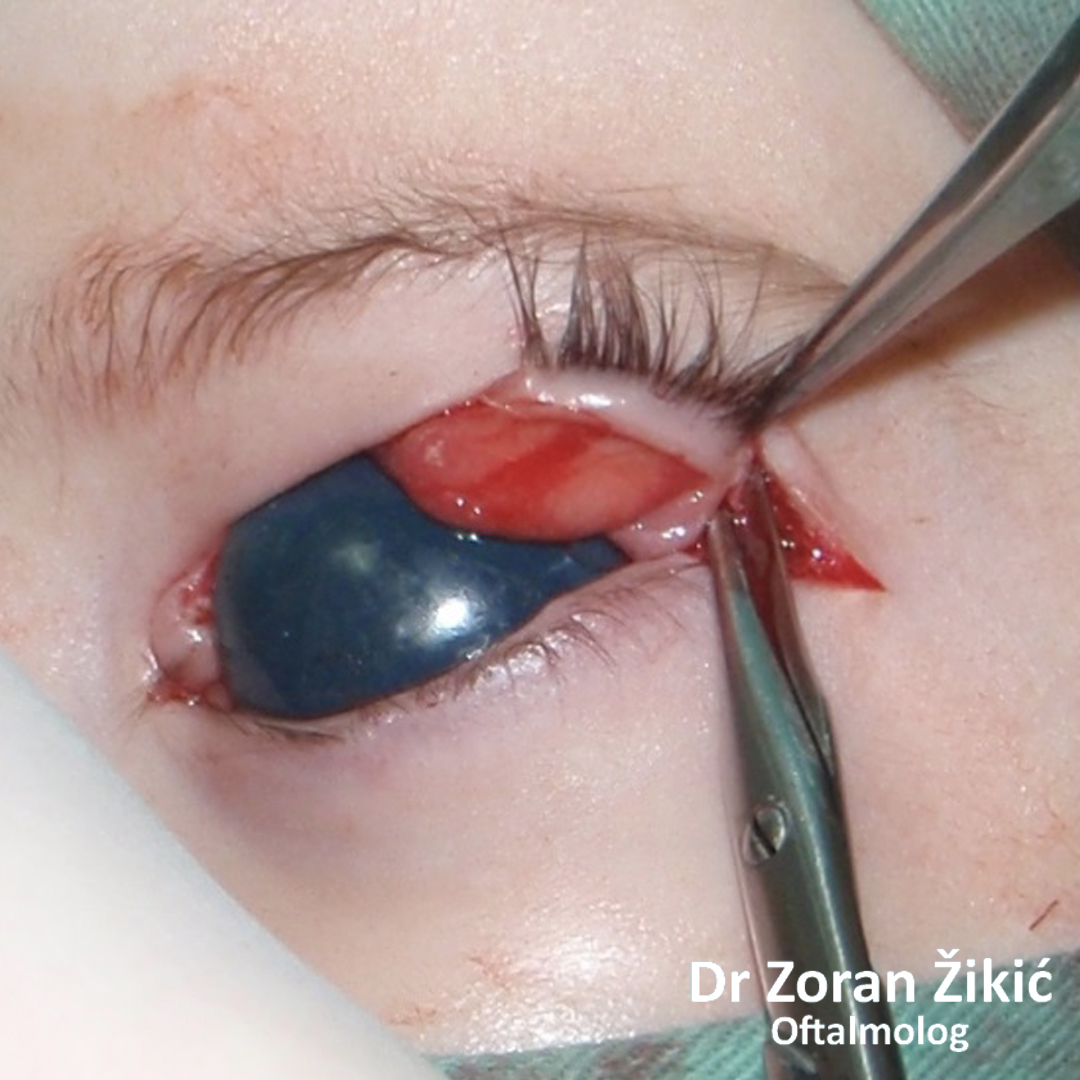
Capillary hemangioma in a small child.
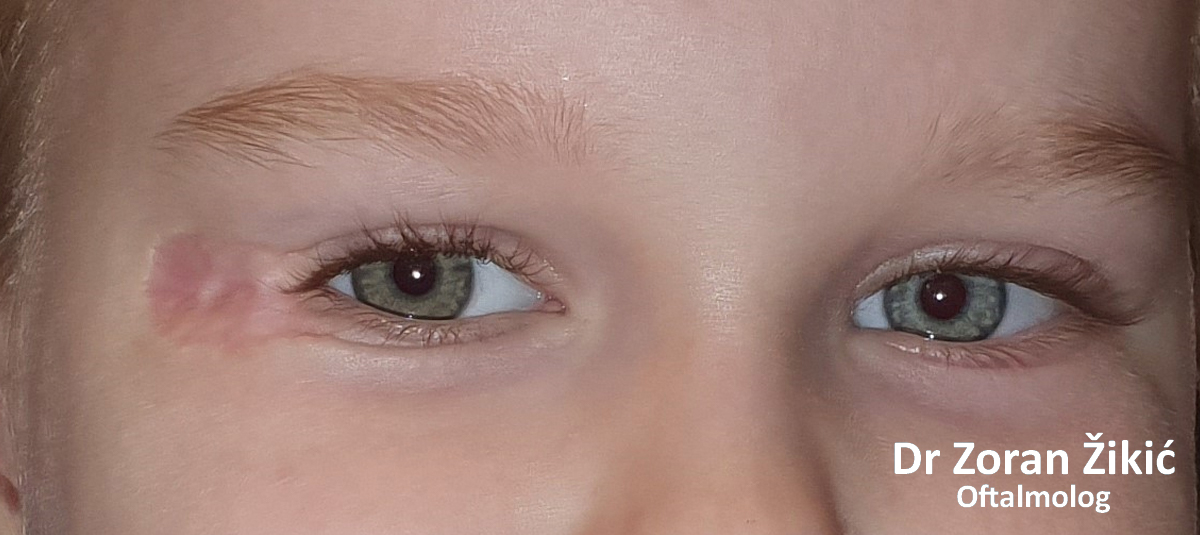
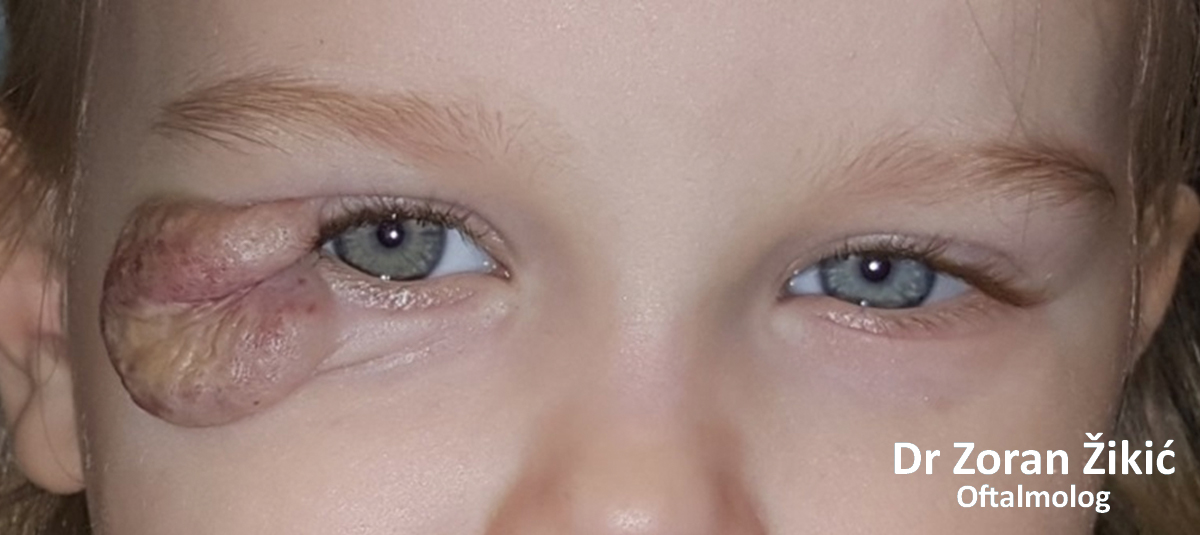
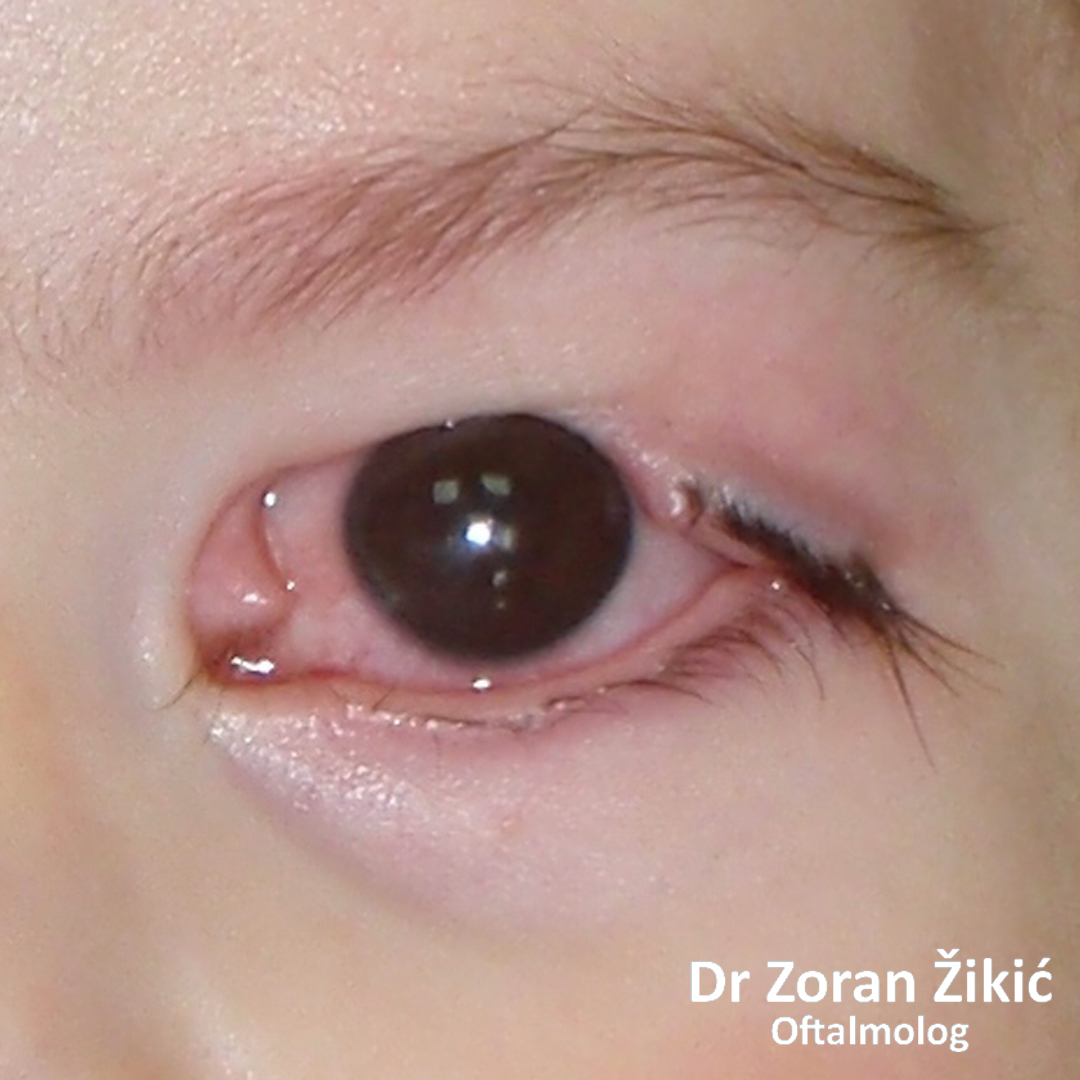
Spontaneous involution of hemangioma, with residual skin and connective tissue.
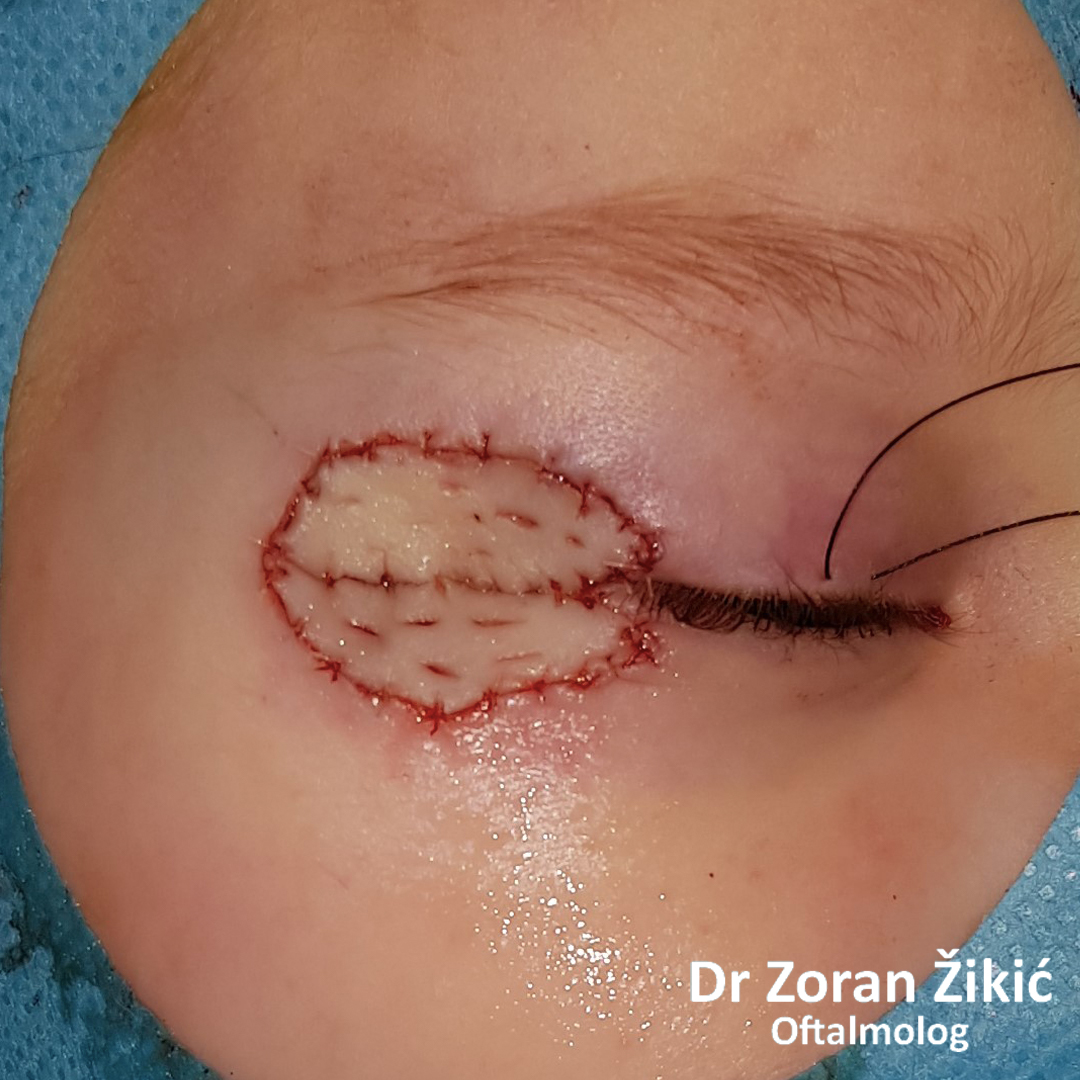
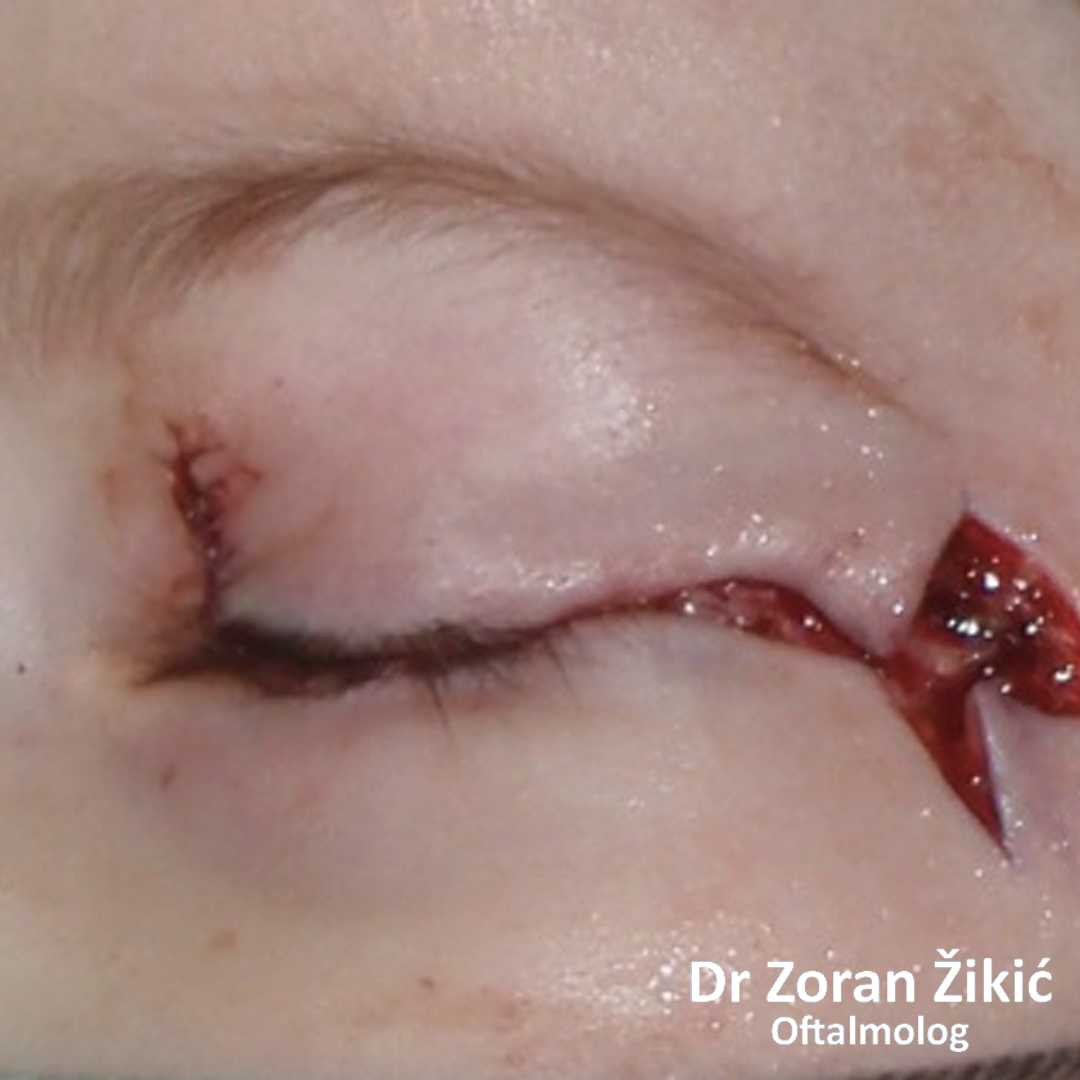
After exscicion and skin grafting from behind both ears.
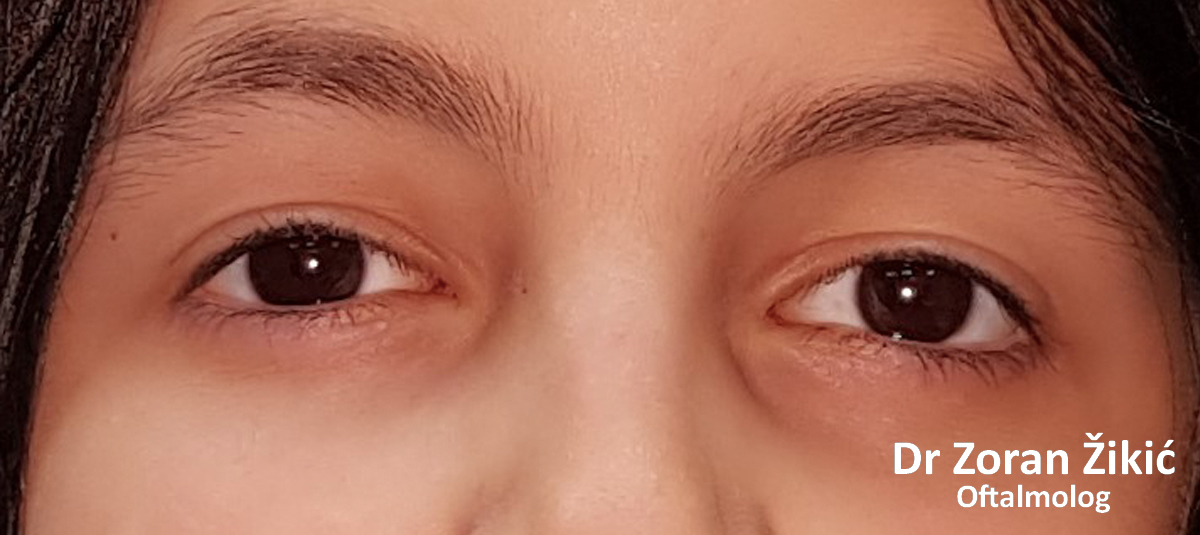
One month after the operation.
Six months after surgery.
Barely visible scar behind ear.
CORRECTION OF CONGENITAL EYELID DISORDERS
Congenital defect of pat of the upper lid (coloboma).
Lateral tissues are mobilized with McGregor Z-plasty.
One year after reconstruction.
Congenital retraction of the left lower lid.
The lower lid rteractors are recessed
and a hard pallate mucosa graft is placed.
CORRECTION OF A DROOPY LID (PTOSIS)
Congenital ptosis of the left upper lid.
Trans-conjunctival approach to the levator muscle.
Plication (folding) of the levator.
Checking of eyelid height during surgery in local anesthesia.
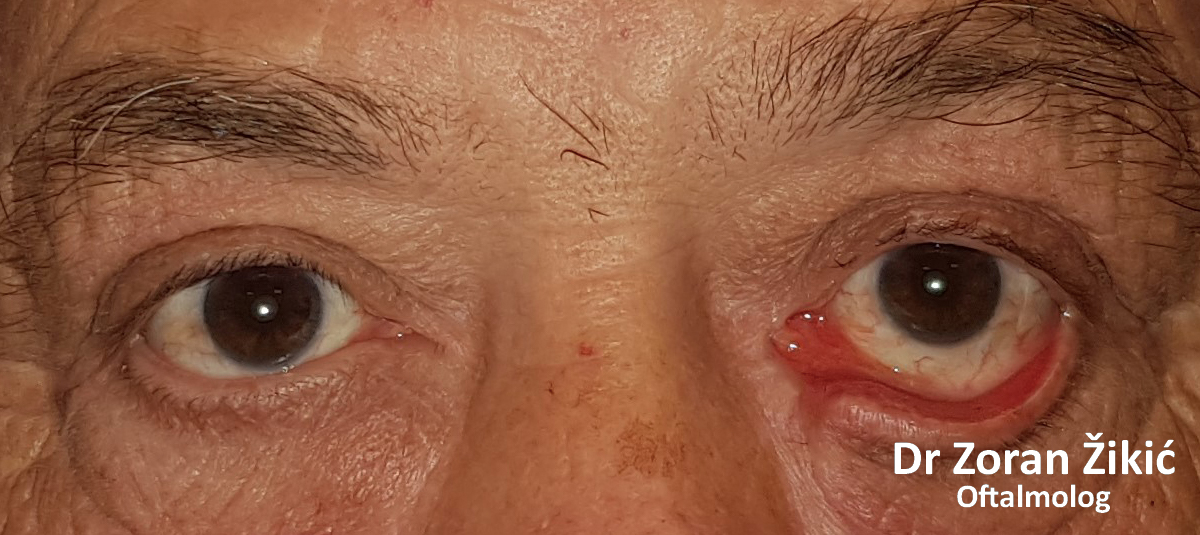
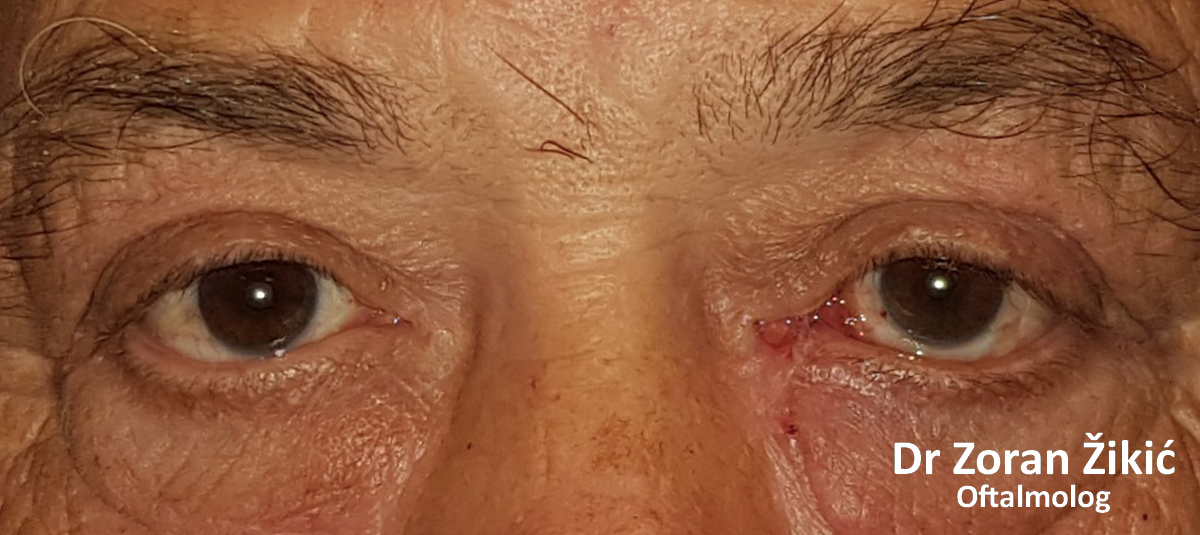
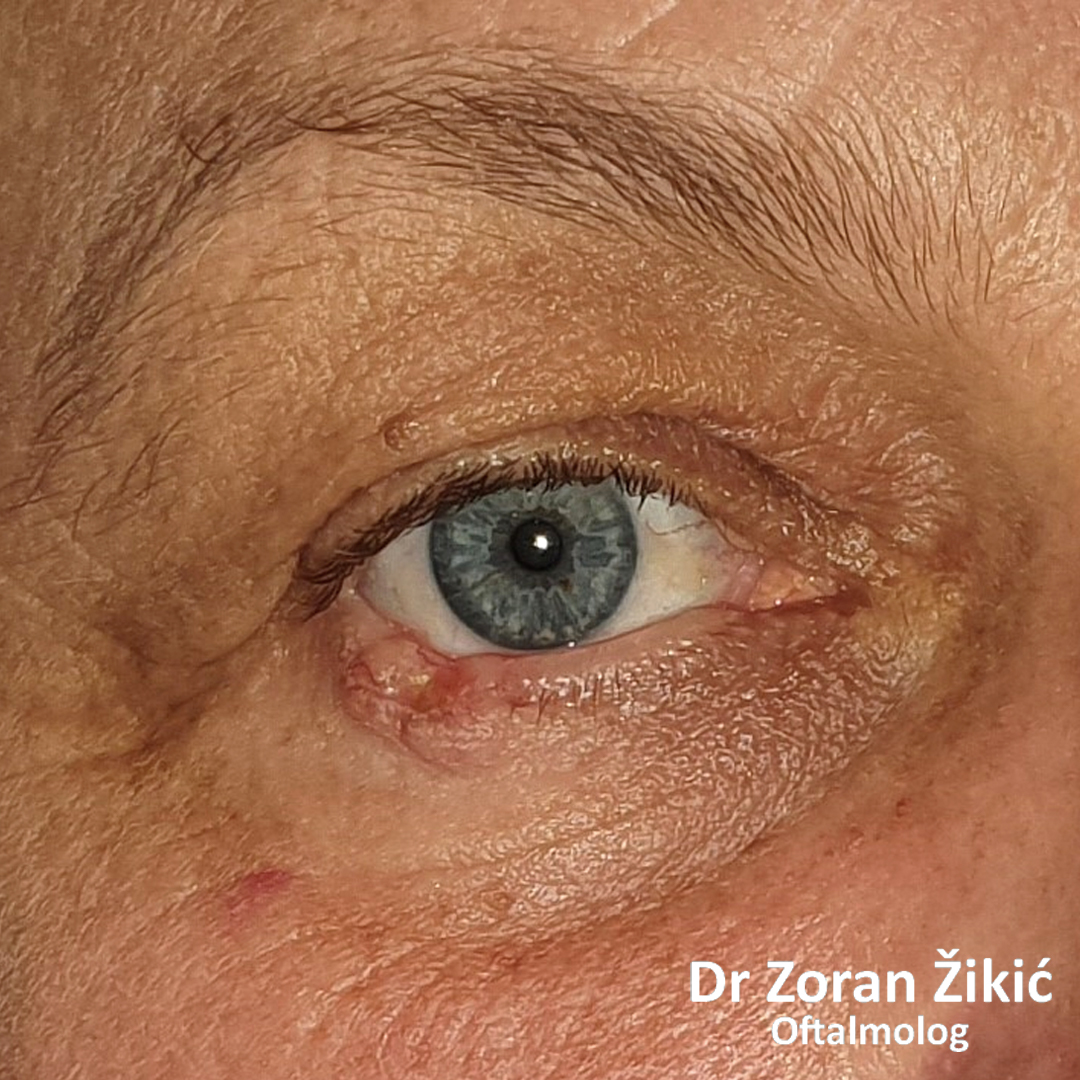
LOWER LID ECTROPION WITH MEDIAL CANTHAL TENDON LAXITY
Long-standing ectropion of the lower lid with a lax medial canthal tendon (MCT).
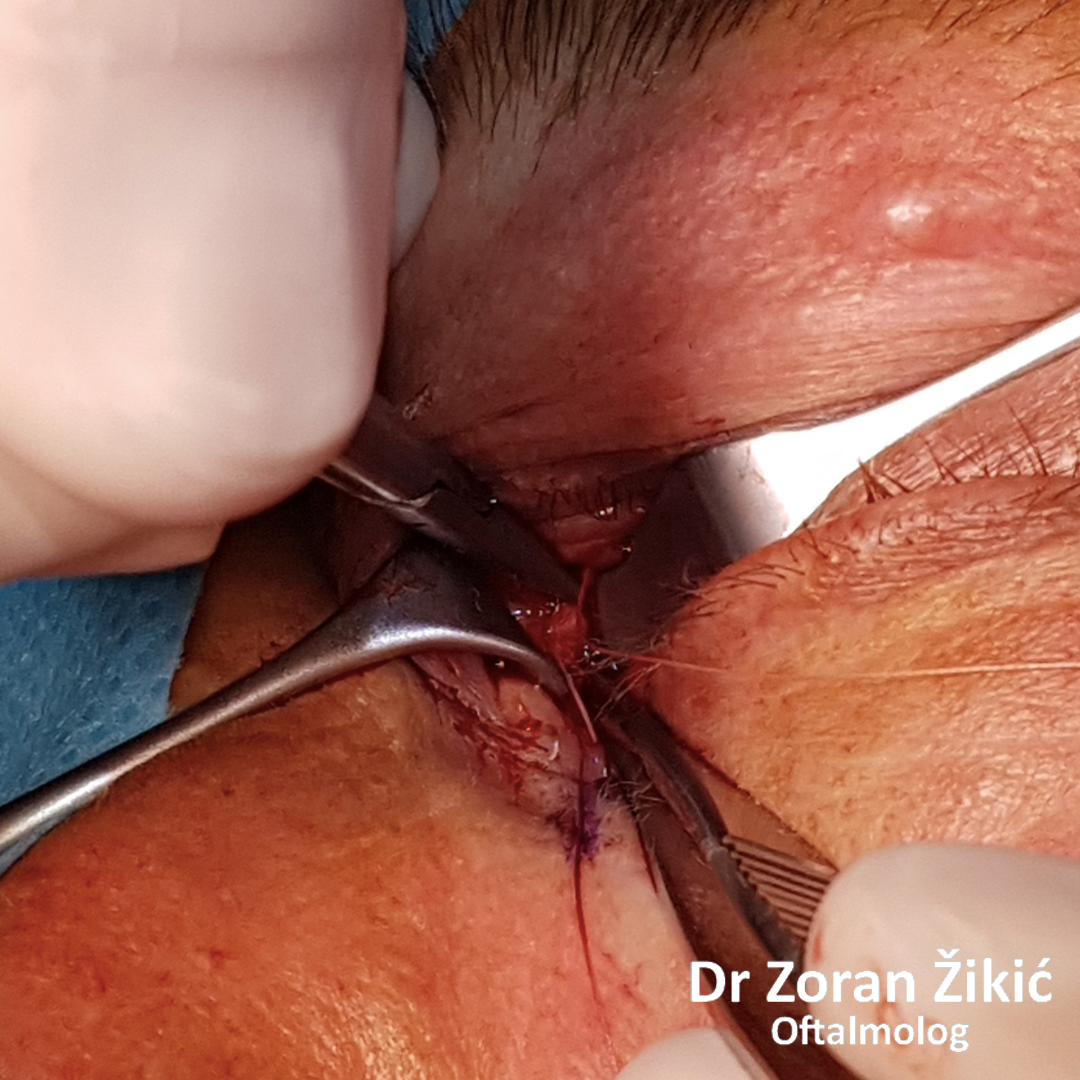
Trans-conjunctival repair of MCT.
EYELID TUMOUR AND RECOSNTRUCTION SURGERY
Basal cell carcinoma of the lower lid.
After tumour resection, the posterior lamella is reconstructed with a tarsal graft from
the upper lid.
The anterior lamela is reconstructed with a sliding skin flap.
The final result of recosntruction.
TEAR DUCTS SURGERY
EXTERNAL DACRYOCYSTORHINOSTOMY (DCR)
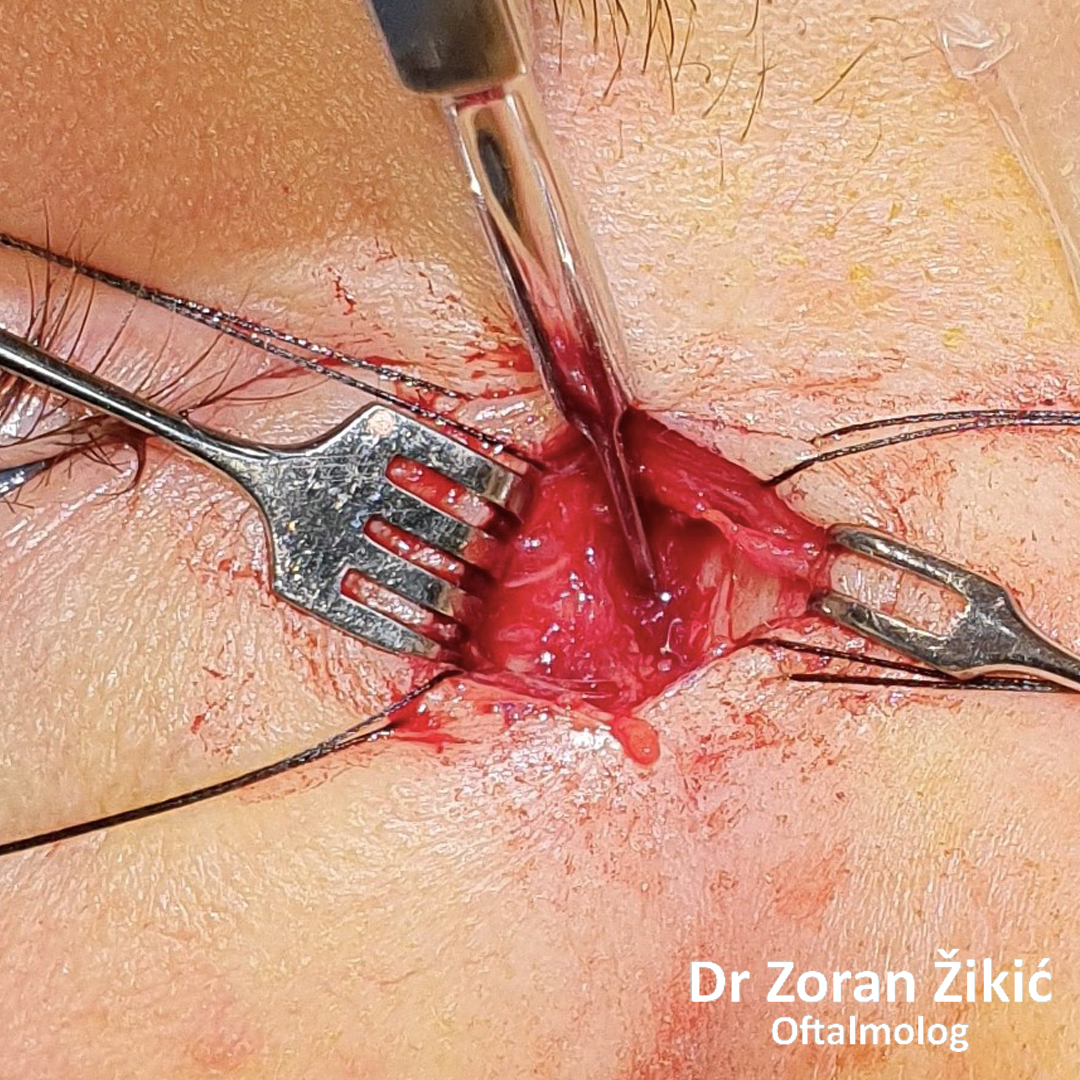
A very enlarged tear sac, due to chronic inflammation.
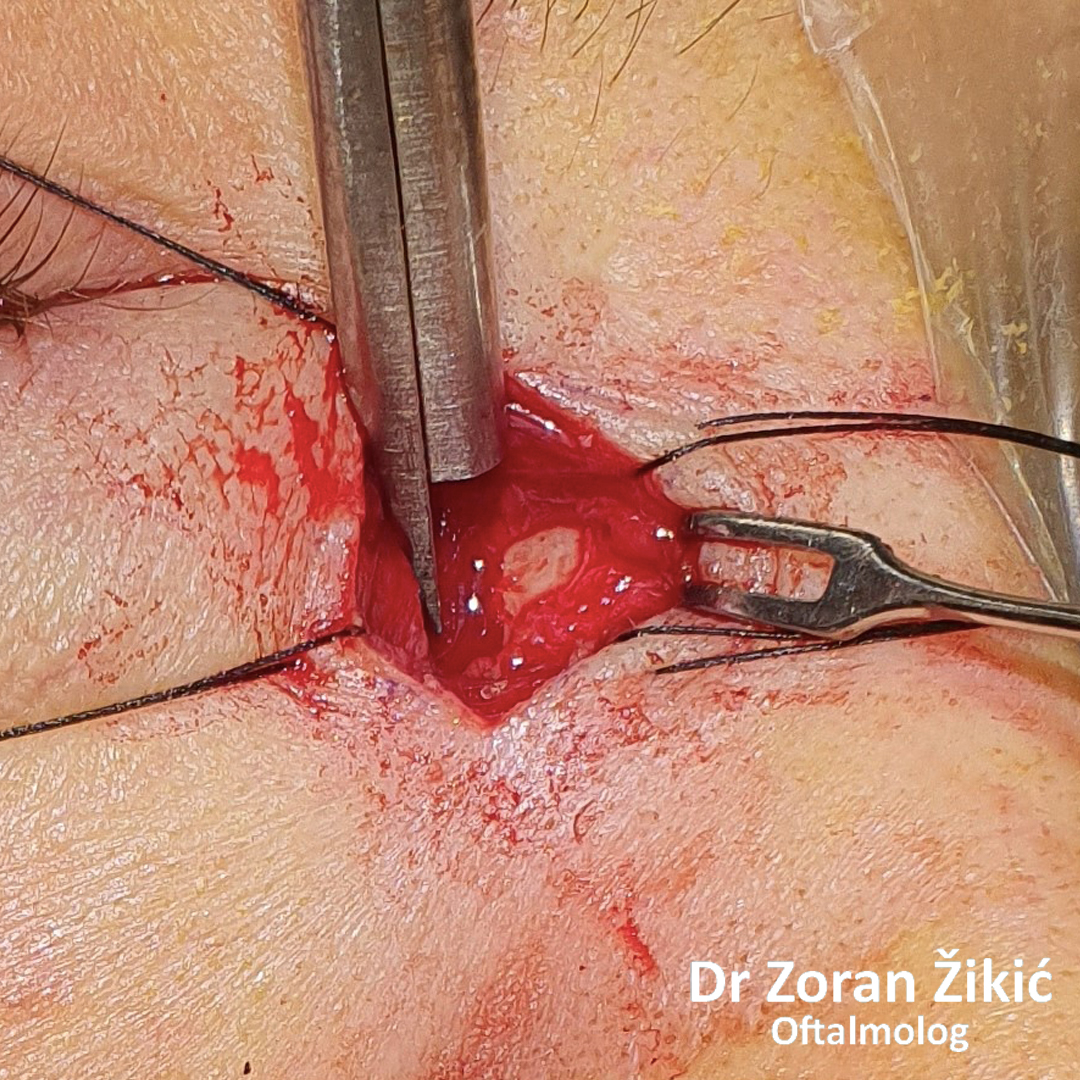
Passage through the thin lacrimal bone.
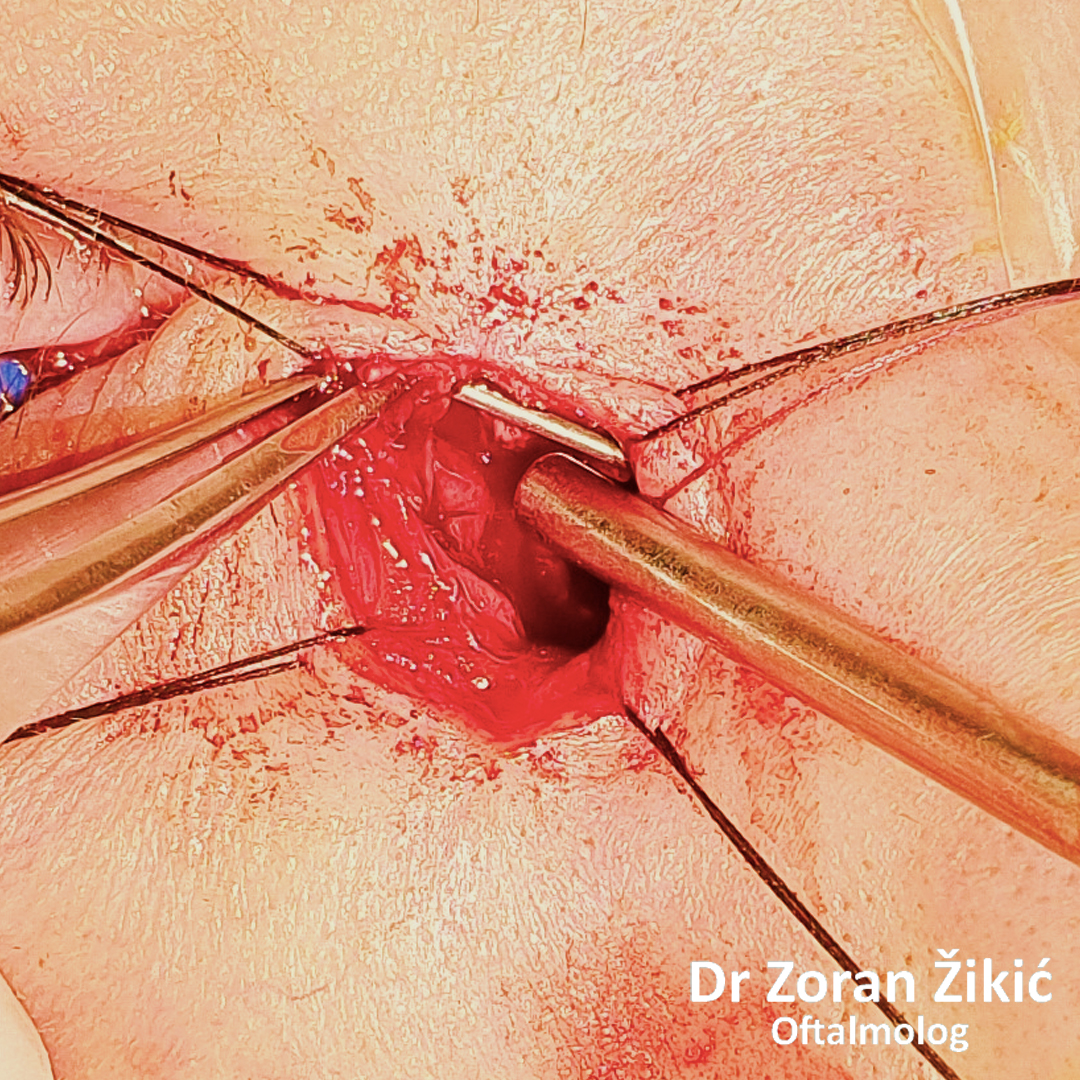
Osteothomy (creating an opening in the thick bone).
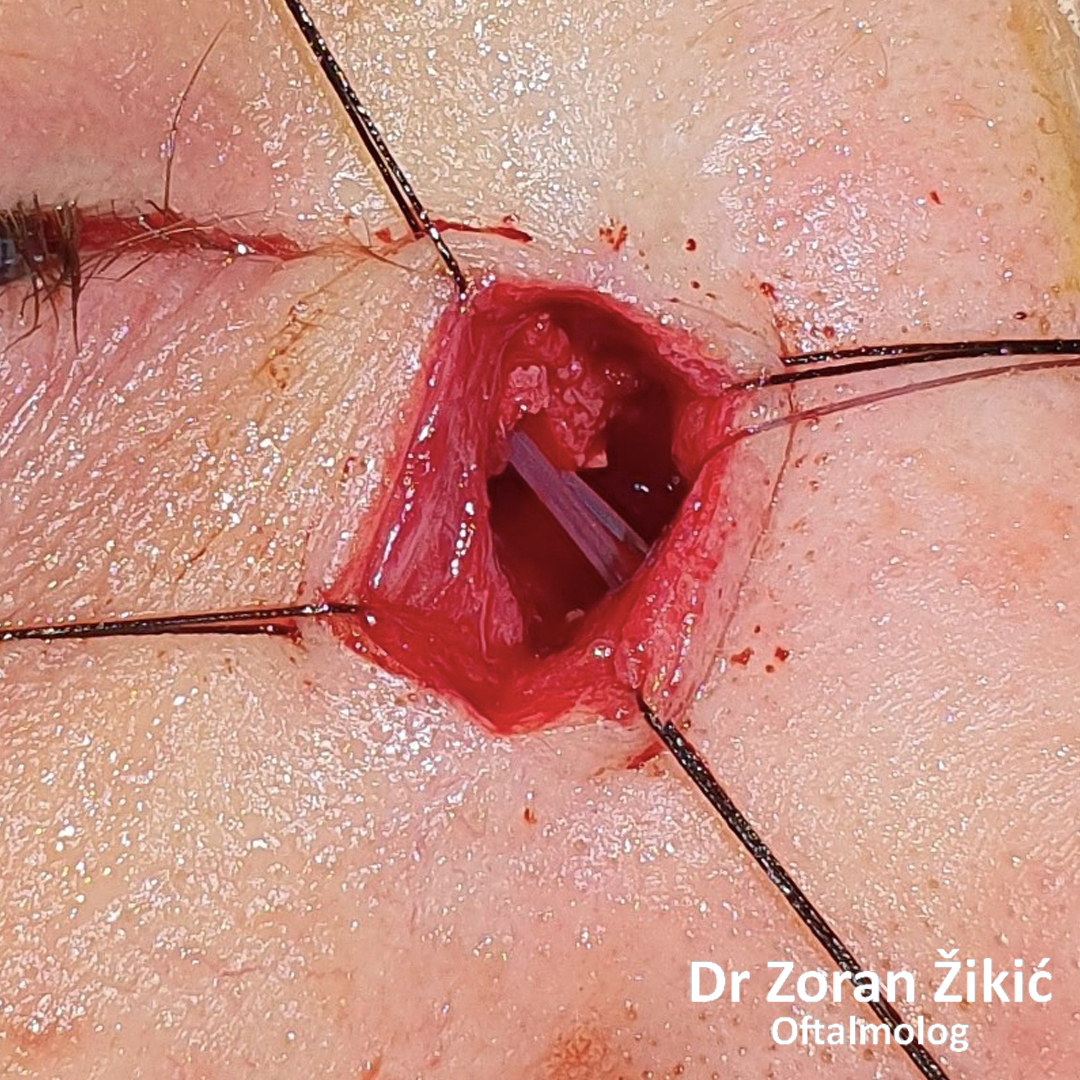
Insercija silikonskog stenta.
Attaching the tear sac to the nasal mucosa.
Barely visible scar one month after the operation.